Lesson 3: Chemical Reactions and Equations
1. Chemical Reactions and Bonding
Chemical changes take place when molecules or elements interact with other elements or molecules to form new chemical compounds. In order for a reaction to take place between molecules and or atoms, these molecules must come into contact with each other. For example, the reaction betting ammonia with hydrogen chloride to form ammonium chloride shown below.
NH3 +HCL → NH4Cl
This equation does not clearly show what has happened. For these molecules to react, the pair of electrons on nitrogen must collide with the hydrogen atom of the HCl. This collision must not only be precise as to the angle of the collision, but it must also have enough energy to break the bond between the hydrogen atom and the chlorine atom and form a new bond between the hydrogen atom and the nitrogen atom. Energy is released when a bond is formed.
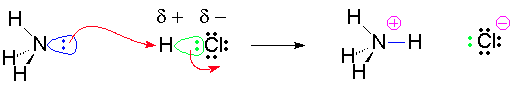
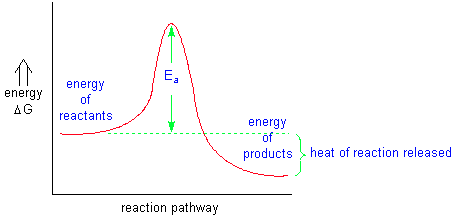
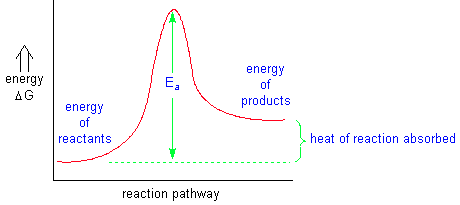
The reaction rate is measured by the change in concentration of one of the reactants or products over a measured period of time. Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to visualize the energy changes in chemical reactions. Some initial energy must be applied to any reaction in order to get the reaction started. This energy is called the energy of activation(Ea).
If a reaction releases more energy than it takes to keep it going, it is called an exothermic reaction. If a reaction requires a constant application of energy to keep it going, it is called an endothermic reaction.
A catalyst is something that, when added to a chemical reaction, will increase the reaction rate without undergoing a permanent change. Although it appears that only Ea is lowered for a catalyzed reaction, the actual reaction pathway must change due to the involvement of the catalyst with the reactants. The energy released for the reaction remains the same. Catalysts are used extensively in biochemical reactions in order to decrease the energy demands for the animal or plant.
The law of conservation mass states that matter can neither be gained nor lost in a chemical reaction. The number and type of atoms in the reactants must exactly equal the number and types of atoms in the products. The arrangement of the atoms will be different because new compounds are formed.
Key Concepts
Chemical reactions
Balancing chemical reactions
Chemical amount

Learn more: study Textbook reading p. 46-63