Lesson 4: Chemical Bonding and Diversity of Matter
3. VSEPR Theory
Structural Diagrams
Structural diagrams are visual representations of a chemical compound that shows the relative placement of every atom with the compound. Covalent bonds are represented by the pairs of electrons shown between the Lewis symbols. Covalent bonds can also be represented using a line to represent each shared pair of electrons. For example, the structural diagram for fluorine (F2) would be written as F–F.
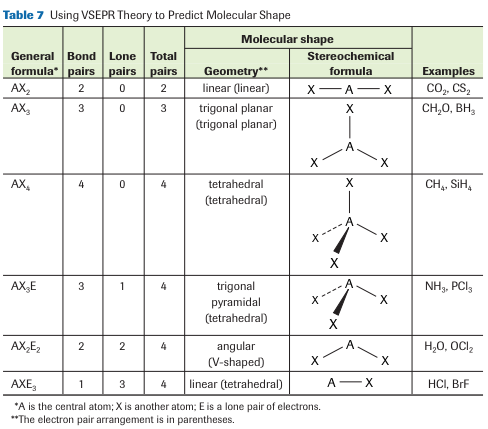
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSERP) theory is used to predict the shape of atoms surrounding the central atom of a molecule. According to VSERP theory;
- Only the valence electrons of the central atoms are important for molecular shape
- Valence electrons are paired in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
- lone pairs and bonding pairs around a central atom move as far apart as possible to minimize repulsion
- Lone-pair electrons repel with greater force than bonding-pair electrons, creating wider angles around lone electron pairs
- Multiple bonding pairs are treated as though they were single bonding pairs.
The VSEPR theory to predict molecular shapes. First, we draw Lewis formulas of the molecule, and then we rearrange all of the pairs of valence electrons to complete octets for all species involved. The key idea is that all the pairs of valence electrons repel each other and try to get as far from each other as possible. Learn more, study textbook pages 91-94.
![]() Did you know that round shape molecules are better mosquito repellent than the other shapes? Research has shown that round-shaped molecules seem better able to block the sensory nerves in the mosquito's antennae.
Did you know that round shape molecules are better mosquito repellent than the other shapes? Research has shown that round-shaped molecules seem better able to block the sensory nerves in the mosquito's antennae.