Social Studies 20-1 Review (copy)
4. Related Issue 3: To What Extent Should Internationalism be Pursued?
Nations, Nation-States and Internationalism
Internationalism is a political movement that advocates a greater economic and political cooperation among nations for the theoretical benefit of all. Partisans of this movement claim that nations should cooperate because their long term mutual interests are of greater value than their individual short term needs.
Internationalism is, by nature, opposed to ultra-nationalism. It teaches that the people of all nations have more in common than they do differences, and this that nations should treat each other as equals.

Nations and nation states have many common and conflicting motives. Some nations prefer to concentrate on their domestic policies and virtually ignore the international community, while others are more concerned with global issues. These countries attempt to not only further their own interests through trade, collective security and other methods but they also attempt to assist in alleviating problems globally.
Common Motives of Nations and States Include:
Economic Stability
Peace and Security
Self-Determination
Humanitarianism
- All humans share the same needs and wants. Everyone needs food, water, shelter to stay alive and healthy. Wants are the things that people desire to have even if they do not require it to survive. Needs and wants create a motive for people to go out and find jobs so they can make money, to fulfill these needs and wants.
- Nations work the same way. Governments are motivated to fulfill the needs of their citizens by trying to provide economic stability. Peace and security, self-determination, and humanitarian activities.
- Abraham Maslow believed that people followed a unique pattern or hierarchy. He believed that once people have satisfied their basic needs, they can focus on their wants.
 I
I
Economic Stability
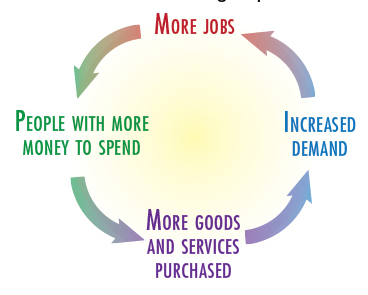
Positive effects of high employment. If there are more jobs there are
more people with money to spend. If companies have more people buying
their products there is more demand, which means that there is a higher
demand for the companies to produce more products. In order for a
company to make more products, they need to hire more people to work,
and so the cycle continues.
Peace and Security
Abraham Maslow believed that safety and security was the second most
important need, because it’s hard to be happy if there is a war going on
in your backyard. Many counties have charters or rights so that people
know that they have the right to live safely. This also helps settle
legal disputes. Countries also have armies or military forces that
protect the country.
Self Determination
Most people like to control their own lives so when governments do not
allow this to happen, the sovereign nations begin to emerge and start
their own country. This is common when some nations only allow one
religion to be followed in the country.
Humanitarianism
- Many people in the world feel sympathy for those who are less fortunate. These people start organizations like food banks so they can help out the less fortunate.
- Natural disasters, disease, wars and conflict can all cause suffering for people. Disasters such as tsunamis can destroy towns in a matter of seconds, killing many people and leaving others injured or stranded.
How do the motives of nations and states shape their responses to the world?
- Countries' withdrawal from contact was one of the reasons Adolf Hitler expanded Germany’s territory, and continued to persecute the Jews.
- A country's complete isolation from the rest of the world is known as isolationism. Japan was a good example of that until 1854, when the United States started trading with them.
- Unilateralism was an issue after WWII, because a nuclear arms race started, and countries just decided to disarm their nuclear weapons to avoid nuclear war.
- Bilateralism is an agreement, or a goal that two persons, or countries can work together, to accomplish, a goal such as Canada and the United States trying to fight against global warming.
- Multilateralism is when countries gather together because of an interest or common goal that they can work together to accomplish.
- Supranationalism is when countries change something so they are more uniform. Ex. The majority of European countries adapted to using the Euro. (previously, they all used separate currencies
Please watch this crash course video discussing American Foreign Policy as it highlights many of the motives of nations and nation states (economic stability, peace and security, etc) as well as the different methods countries use to achieve their national interest (such as isolationism, bilateralism, etc).
In
countries with dictators, setting foreign policy is relatively easy
because they can make decisions without consulting the people.
With
democracies, setting foreign policy is a more complex process that must
reflect the beliefs, values and goals of the country's citizens.
Clear foreign policy goals help guide the actions of the government. In 1995, foreign affairs and international trade Canada published a review
of the Canadian foreign policy. This report highlighted the importance
of setting goals that reflect the values of a country's citizens. It
said, "only states with clear objectives, acting on a strong domestic
consensus, will be able to deploy significant influence and play an
effective role in this new world."
Internationalism and Nationalism
Many of the forces that shape globalization such as trade,
transportation and improved communications also shape the growth of
internationalism. Each of these forces increases contact among
countries at both governmental and non-governmental levels. Some people
believe increased contact to have both positive and negative
consequences. It may promote internationalism and cooperation among
countries but it may also erode the sovereign power of nation states.
Please go through the PPT below to review more about how changing world conditions promote the need for internationalism. This information will be useful to you in Social Studies 30, when you look at contemporary issues through the lens of whether or not liberalism is viable.
Internationalism and Nationalism PPT
In summary, many contemporary global issues are so complex that even national governments are unable to deal with them. For this reason, countries often choose to work with the international community to tackle challenges such as poverty, hunger, disease, debt, climate change, human rights and conflict.