Module 6 Mendelian Genetics
Lesson 3.6.9
3.6.9 page 2
 Read
Read
Recall from our lesson on sex linkage that Thomas Hunt Morgan provided experimental evidence that genes occur on chromosomes. This discovery immediately creates a new idea from Mendel’s laws; the idea that traits could tend to move together if they were on the same chromosome.
Mendel did not find this with any of his seven traits. For Mendel’s work, each trait had no relation to another. Each assorted independently. It turns out that each of his traits were found on different chromosomes, so we would expect them to move independently.

Many traits in organisms have now been found to in fact be coded for on the same chromosome. These genes coding for such traits do tend to move together, and are thus called “linked genes”. When first considering linked genes, you may think that these genes always move together, however that is not the case. Even though they are on the same chromosome, there is a process that can exchange pieces of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. You may recall from our lessons on meiosis that this process is called crossing over. The farther apart two genes are on a chromosome, the greater the number of cross over events that will occur between them, and it is less likely that the two traits will move together. The number of crossover events directly relates to distance on a chromosome. Read about linked genes, crossing over and chromosome mapping on pages 599 – 601 of your text.
 Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
Consider the following video of a lecture in genetics at MIT.
- How is the phenotypic ratio of the cross GgRr × ggrr different for Independent Assortment than for linked genes (Chromosomal theory)?
- What is meant by “parental types” of chromosomes?
- What is meant by “non-parental types” of chromosomes?
- How does recombination frequency relate to map distance
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Answer the following questions to check your understanding of the material covered up to this point.
- If there were 50 recombination phenotypes in 250 offspring, what is the map distance between the linked alleles?
-
A three-point test cross is performed to identify the locus of each of three alleles in relation to one another. The results were as follows:
- AC recombinations = 225
- BC recombinations = 165
- AB recombinations = 60
- Parental linkages = 550
- Total offspring = 1000
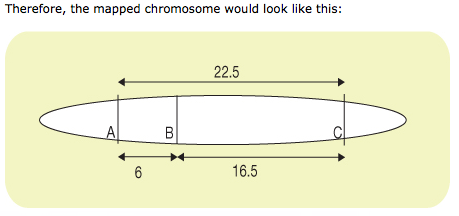
Show the positions and map the distances apart for each allele (A, B, and C) on a chromosome. Calculate the map units, then draw the chromosome.
- Crossover % = 50/250 x 100 = 20%
Since 1% crossover represents 1 map unit, 20% crossover would mean 20 map units apart.
- The cross over percentages and map units are as follows.
• AC = 225/1000 x100 = 22.5% or 22.5 map units
• BC = 165/1000 x 100 = 16.5 % or 16.5 map units
• AB = 60/1000 x 100 = 6% or 6.0 map units