Module 5
1. Module 5
1.17. Page 2
Module 5: Angles
Get Started
In this activity you will review several angle relationships that you examined in previous math courses.
 Try This
Try This
Work with a partner, if possible.
Step 1: On a blank sheet of paper, draw a triangle of any shape and size. Label the angles as shown, and measure the angles with a protractor. Record these measures.
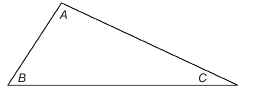
Step 2: Cut out the triangle, and then tear off ∠B and ∠C.
Step 3: Place ∠B and ∠C next to ∠A so that all three vertices lie at the same point.
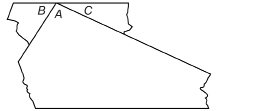
Notice that the three angles at A form a straight line. Do you remember that the measure of a straight angle is 180°?
 Self-Check
Self-Check
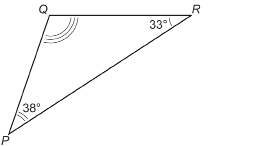
SC 1. Calculate ∠A + ∠B + ∠C. Will this sum be the same for any triangle you draw? Why?
Next, you will apply this relationship among the angles of a triangle.
Example 1
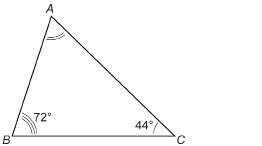
Find the missing measure of ∠A.
Solution
In a triangle, all the angles add up to 180°, so you know that the following is true: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°. Use this information to find the value of ∠A.
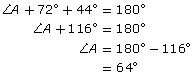
Then check your answer.
![]()
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 2. Find the missing measure. When finished, check your answer.