Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.10. Explore 6
Module 3: Quadratics
Suppose you are given the vertex of a parabola (6, 8) and one of the x-intercepts (2, 0). From this information, you can determine the following:
- the coordinates of the other x-intercept
- whether the value of a in the quadratic function is negative or positive
- the maximum or minimum value of the function
This information can be determined without drawing the graph by using the axis of symmetry and some reasoning. Since the vertex is at (6, 8), the axis of symmetry is at x = 6. The given x-intercept (2, 0) is 4 units to the left of the axis of symmetry (6 − 2 = 4). Therefore, the other x-intercept will be 4 units to the right side of the axis of symmetry at x = (6 + 4), or x = 10.
Remember that the value of a in the quadratic function y = ax2 + bx + c indicates whether the parabolic graph of the quadratic function opens upwards or downwards. If a is positive, the graph opens upwards and the vertex is the minimum value of the function. If a is negative, the graph opens downwards and the vertex is the maximum value of the function. The given x-intercept (2, 0) is below the vertex (6, 8); so the graph must open downwards. This tells us the value of a in the quadratic function is negative and the vertex is a maximum.
Therefore, the maximum value of the function is 8, the value of y at the vertex.
Self-Check 3
- Use the following graph to complete this question.
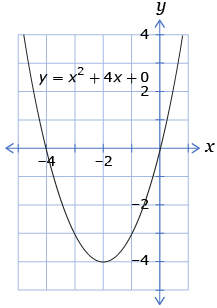
For the graph, describe the
- vertex
- direction of opening
- axis of symmetry
- domain
- range
- x-intercepts
- y-intercept
- maximum or minimum value of the function
Answer
- vertex
- Use the following graph to complete this question.
 For the graph, describe the
For the graph, describe the
- vertex
- direction of opening
- axis of symmetry
- domain
- range
- x-intercepts
- y-intercept
- maximum or minimum value of the function
Answer
- vertex
- Using the principles of symmetry, sketch the graph of y = −2x2 +16x − 16. Use the following information to sketch your graph:
- The vertex is at (4, 16).
- One point on the graph is (2, 8).
- Another point on the graph is (0, −16).
Answer
Did you notice that the y-intercept is the same as the value of c in the standard form of the quadratic function y = ax2 + bx + c? Look back at the graphs in Self-Check 3. Observe how the constant at the end of the function is always the y-intercept. That will always be true.
To see why, put the value of 0 in for x in the standard form of the quadratic function.
y = ax2 + bx + c
y = a(0)2 + b(0) + c
Can you see that for a quadratic function in standard form, the y-intercept will be y = c?
If you haven’t done so already, you may want to add the characteristics of quadratic functions that you studied in this lesson to your notes organizer. Check out “In Summary” on page 332 of the textbook for some key ideas and concepts that were covered in this lesson.
Self-Check 4
If you feel you need a bit more practice, you may complete all or parts of “Check Your Understanding” questions 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 on pages 332 to 334 in the textbook. When you finish a question, check your work using the shortened answers given on page 550 at the back of the textbook. If you are still unclear about how to answer some questions, make sure to contact your teacher to get some assistance.
Recall from the Course Introduction that you will be creating your own course glossary. Open the Glossary Terms document that you saved to your course folder, and add in any new terms. You might choose to add the following terms to your copy of Glossary Terms:
- maximum value
- minimum value
- vertex
- x-intercept
- axis of symmetry