Module 7
1. Module 7
1.19. Page 2
Module 7: Trigonometry
Get Started
In this activity you will review how the sine ratio is used to find either the side opposite or hypotenuse if given the other side and an acute angle in a right triangle. Also, you will review how to find the acute angle if both the opposite side and hypotenuse of a right triangle are given.
 Try This
Try This
Work with a partner, if possible.
You will use the “Exploring Trig Ratios” math interactive to review how to apply the sine ratio to find a missing side or angle in a right triangle. Note these tips:
-
Make sure you are in “Explore It” mode.
-
Select the “sin R” function to explore.
-
Choose the “Unknown side or angle” in the right triangle.
-
Resize the triangle by using the “Scale slider” or by dragging the vertices.
TT 1. Examine the steps used to solve for the unknown. How do the steps for solving for an unknown angle differ from finding an unknown side?
Now you are ready to explore problem situations involving the sine ratio.
Share
With a partner or in a group, discuss your answers to TT 1. How does solving using the sine function to find an unknown side differ from finding an unknown angle? Are the steps different? How so? Explain.
Summarize your discussion, and save a copy of your summary in your course folder.
Explore
In this activity you will determine the height of a hill in your neighbourhood. The hill could be along a straight road in the countryside or along a valley near where you live.
 Try This
Try This
In this Try This activity you will need your clinometer, a tape measure, and your calculator. Work with a partner, if possible.
Step 1: In your neighbourhood, select a hill along a straight stretch of road or overlooking a valley. You are going to determine the hill’s height by using the sine ratio! The hill you select should be as uniform in slope as possible (i.e., not too bumpy—one straight hill).
Step 2: From the base of the hill, measure the hill’s angle of elevation using your clinometer. You may wish to measure the angle several times and average your results to ensure accuracy.
Step 3: You will also need to measure the length of the hill’s slope. For a short slope you can use a measuring tape. For longer slopes you may have to pace off the distance or, if the hill is along a straight stretch of road, it may be possible to use the odometer of a car or truck. Then complete TT 2 to TT 4.
TT 2. Using your measurements, draw and label a diagram that describes your situation.
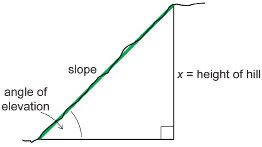
TT 3. Use the sine ratio to calculate the height of the hill (x). Show all steps.
TT 4. How accurate is your calculated answer? What could you have done to improve the accuracy? Contact your teacher to discuss the answers.