Module 7
1. Module 7
1.20. Page 3
Module 7: Trigonometry
Bringing Ideas Together
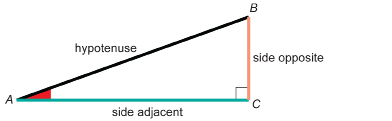
In Explore you looked at indirect measurement and the sine ratio. You used the following relationship to find the height of the selected hill.
![]()
This relationship can be used as you did in Explore to find the side opposite. This relationship can also be used to determine the hypotenuse or the reference acute angle in a variety of problem situations. Study these examples.
Example 1
A 25-ft-long wheelchair ramp is inclined at an angle of 4.6° to the horizontal. From the foot of the ramp to the top, what is the vertical rise? Round to the nearest tenth.
Solution
Draw a diagram.
![]()
Let x be the vertical rise.
Substitute into the formula.
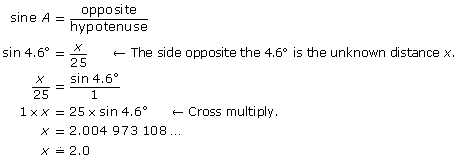
The vertical rise of the ramp is approximately 2.0 ft.
Example 2

© BORTEL Pavel/shutterstock
A ladder leans against a vertical wall. The foot of the ladder is positioned for safety at an angle of 75° with the ground. The ladder reaches 14.5 ft up the wall. To the nearest foot, what is the length of the ladder?
View the animated “Ladder Solution.”
Example 3
A mountain trail used by cyclists to train on drops 235 m from the trail head to the bottom over a trail distance of 1.1 km. To the nearest degree, what is the average slope of this trail?
Solution
Do you remember how many metres are in a kilometre? Review “SI Length Conversion” if you need a refresher.
Draw a diagram.
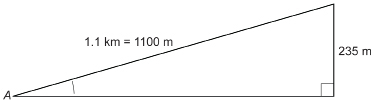
Let ∠A be the required angle.
All distances must be in the same units.
![]()
Substitute into the formula.
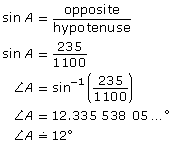
The average slope of the trail is approximately 12°.
Practise these skills!