Module 7
1. Module 7
1.36. Page 3
Module 7: Trigonometry
Bringing Ideas Together
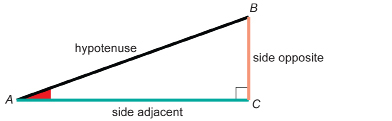
In Explore you applied the definitions of sine, cosine, and tangent to find missing sides and angles.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Did you use SOH-CAH-TOA to help you recall these definitions?
solve a right triangle: to find all the missing sides and angles in a right triangle
You will now apply these definitions in problem situations where you have to solve a right triangle.
In Example 1 you are given the measure of one side and one angle of a right triangle. From this information you will find the missing sides and angles.
Example 1
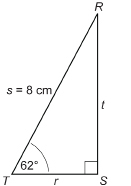
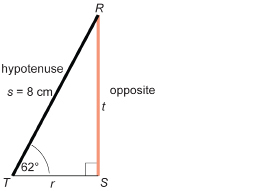
In ΔRST, ∠S = 90°, ∠T = 62°, and s = 8 cm. Solve ΔRST. Round to one decimal place when appropriate.
Solution
Draw a diagram.
∠R |
|
∠T |
62° |
∠S |
90° |
Side s |
8 cm |
Side r |
|
Side t |
You must find ∠R and sides r and t.
Remember that all the angles in a triangle add up to 180°.
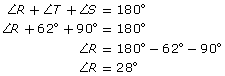
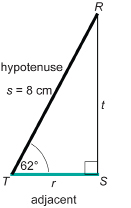
Next, find side r.
Side r is adjacent to the given angle, ∠T. You know the hypotenuse, s.
SOH-CAH-TOA
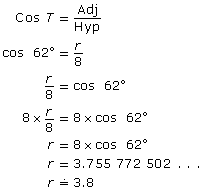
Side r is approximately 3.8 cm.
Lastly, find side t. Side t is opposite to the given angle, ∠T. You know the hypotenuse, s.
SOH-CAH-TOA
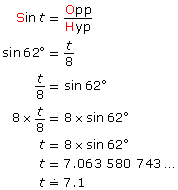
Side t is approximately 7.1 cm.
In Example 2 you are given the measure of two sides in a right triangle. From this information you will find the missing side and all the unknown angles.
Example 2
In ΔDEF, ∠F = 90°, d = 5 cm, and f = 8 cm. Solve ΔDEF. Round to one decimal place when appropriate.
View the animated “Solving a Triangle: Triangle DEF Solution”
As you may have noticed, there are many ways to solve these problems. Depending on the order you solved for the unknowns, you may have chosen different trigonometry ratios to find the unknowns. Ultimately, whatever methods are used, the final solutions for the unknowns will be the same.