Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.10. Lesson 2 Summary
Module 5: Radicals
Lesson 2 Summary
To convert entire radicals, whether or not they include variables, to mixed radicals, you can use prime factorization. Or, if the radicand has a factor that is a perfect square or a perfect cube, you can factor out the greatest perfect square or perfect cube.
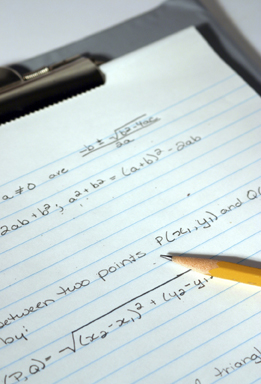 iStockphoto/Thinkstock
iStockphoto/Thinkstock
When there are variables present in a radical, you have to consider what values will ensure that the solution is a real number. When you do this, you need to state whether there are restrictions on possible values of the variable. It is important to keep in mind the index of the radical when you do this. If the index of the radical is even, then the radicand cannot be a negative number. For example, ![]() If the index of the radical is odd, then the radicand can be a negative number. For example,
If the index of the radical is odd, then the radicand can be a negative number. For example, ![]()
In the next lesson you will learn how to add and subtract radicals.