Lesson 8
1. Lesson 8
1.8. Lesson 8 Summary
Module 6: Proportional Reasoning
Lesson 8 Summary
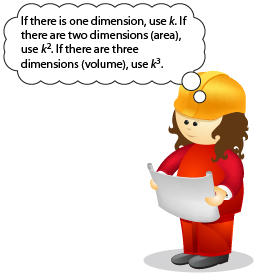
adapted from: iStockphoto/Thinkstock
The process of moving involves a lot of “making sure things fit.” In this lesson you used your understanding of scale factor, area, and volume to solve problems involving 2-D objects and 3-D shapes. You helped Akuti work with scale factors to place her mural in the right place on her wall and make it the correct size. Rajesh needed assistance in making sure his new TV would fit in his entertainment centre before he assembled it.
When trying to determine how dimensions of a 3-D object change with an increase or decrease by a certain factor, an understanding of the relationships among scale factors, area, and volumes is required. In the pool example, you used these relationships to show Mr. Jones that making a 3-D object “25% larger” can mean several things.
You have used proportional reasoning to solve a wide variety of problems in this module. Refer to the Module 6 Summary for an overview of concepts you investigated in this module.