Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.5. Explore
Module 4: Foundations of Trigonometry
Explore
In Discover you saw that each counterclockwise rotation of the terminal arm increases the angle measurement by 2π, or 360°. For each clockwise rotation of the terminal arm, the angle measurement decreases by 2π, or 360°. In Try This 2 you will apply this understanding to determine the distance travelled by a horse.
Try This 2
Sometimes a horse walker is used for horses that need rehabilitation. The horses are tied to a pole at the centre, and they walk at a constant rate around the circular horse walker.
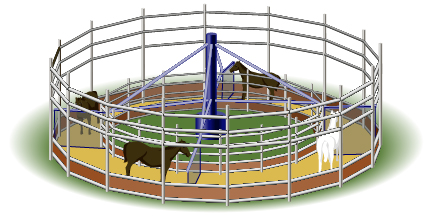
A horse walker has a radius of 6 m. The horses take 12 s to walk 1 revolution.
- What distance does a horse walk after 1 revolution? Place this information in a table similar to the one shown.

- What distance, and through what central angle, will the white horse travel after the times specified in the table?
- Complete the rest of the table.
12 s 24 s 36 s Number of Revolutions 1 Distance Travelled by White Horse to the Nearest Tenth of a Metre 37.7 Diagram of Rotational Angle in Standard Position 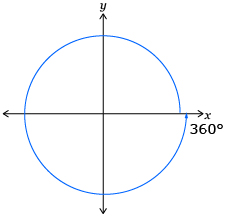
Angle of Rotation in Degrees 360° Angle of Rotation in Radians 2π -
How did you determine the distance travelled by the horse? Explain your process.
- Explain how you found the rotational angle.
- How do the terminal arms for each revolution compare?
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.
The distance around 1 revolution is equal to the circumference of the horse walker.