Lesson 3: Economic Liberalism and Equality
2. Lesson Economic Liberalism and Equality

REVIEW OF CLASSICAL LIBERALISM
Before examining different ideas about economic equality it is important to review the values of classical liberalism, the positive and negative impacts on society, as well as why the shift towards modern liberalism occurred.
To get you thinking about these important questions I would like to remind you of this- in unit 2 you explored the values of individualism and considered how those values are the basis of CLASSICAL LIBERALISM. CLASSICAL LIBERALISM values:
self interest
competition
economic freedom
Then in unit 3 you looked at the consequences of CLASSICAL LIBERALISM which included both pros and cons. These consequences are reviewed in the following chart:
CONSEQUENCES OF CLASSICAL LIBERALISM
PROS
- technology and innovation encouraged
- workers and owners are motivated to earn money and make profits
- competition between companies results in low prices, higher quality, and wider selection of goods
- efficiency is encouraged in use of resources and the operation of companies to keep production costs low
- the economy can respond quickly to change
- When a company is doing well, it can afford to pay its workers well. When there is a shortage of workers, a company will pay higher wages to attract and keep them
CONS
- A wide gap may exist between high and low income earners
- The economy may go through periods of growth and inflation (boom) and recession or depression (bust)
- There may be periods of high unemployment
- Product or service advertising can manipulate consumer demand
- Producers can form monopolies and exert too much control over the marketplace
- Sometimes resources can be used ineffectively, and the costs may affect everyone in society (ie. factory pollution)
- Sometimes resources are wasted on goods that people want, but which they may not need
To get you thinking about these important questions I would like to remind you of this- in unit 2 you explored the values of individualism and considered how those values are the basis of CLASSICAL LIBERALISM. CLASSICAL LIBERALISM values:
self interest
competition
economic freedom
PROS
- technology and innovation encouraged
- workers and owners are motivated to earn money and make profits
- competition between companies results in low prices, higher quality, and wider selection of goods
- efficiency is encouraged in use of resources and the operation of companies to keep production costs low
- the economy can respond quickly to change
- When a company is doing well, it can afford to pay its workers well. When there is a shortage of workers, a company will pay higher wages to attract and keep them
CONS
- A wide gap may exist between high and low income earners
- The economy may go through periods of growth and inflation (boom) and recession or depression (bust)
- There may be periods of high unemployment
- Product or service advertising can manipulate consumer demand
- Producers can form monopolies and exert too much control over the marketplace
- Sometimes resources can be used ineffectively, and the costs may affect everyone in society (ie. factory pollution)
- Sometimes resources are wasted on goods that people want, but which they may not need
The disadvantages of CLASSICAL LIBERALISM resulted in an ideological shift.
Watch the following video to learn about the evolution of MODERN LIBERALISM:
Please complete this worksheet as you watch the video. Include it in your notes for the course. Worksheet.
What is Economic Equality?
So modern liberals recognized that there needed to be changes to their economic policy resulting an ideological shift towards the centre. This shift raised the question - what is economic equality?? Economic equality means various things to various people. Examine the spectrum below. In terms of economic equality, where do you fit?

 I'm a collectivist. I believe that economic equality comes from the following values:
|
 I'm an individualist. I believe that economic equality comes from the following values:
|
|---|
If you believe in the values of collectivism, economic equality means that the group takes care of its individuals for the common good. This usually means that the government has a large role in society, which may limit individual freedoms. Government economic control is important.
If you believe in the values of individualism, economic equality means individuals should have the equal opportunity to use their abilities for their own self-interest. This will benefit the common good. This usually means that the government has a limited role in society, which maximizes individual freedoms. Individual economic freedom is important.
Various Ways to Achieve Economic Equality
Just as various people have various values about economic equality, societies also have various ways of achieving economic equality. The range of methods can be seen in the following diagram.
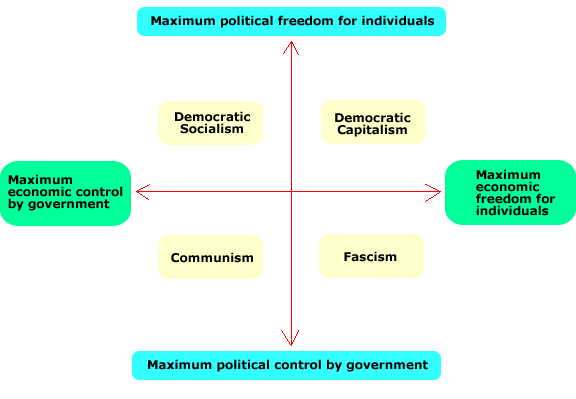
An important point to understand here is the difference between "economic freedom", "economic control", and "economic equality". If a society has economic freedom, it does not necessarily have economic equality. On the other hand, to have government economic control does not mean the society has no economic equality.
Consider the bar graph on the bottom of page 315 in your textbook, Understandings of Ideologies. Among liberal democracies, the United States has the lowest grade for economic equality. Yet, everyone knows that the United States has one of the highest levels of economic freedom in the world. How can a country with a high level of economic freedom have one of the poorest levels of economic equality?
The answer is in the values of individualism and capitalism that the United States holds very strongly. These values promote aggressively self-interest, individual or private ownership of the means of production, and limited government involvement in the economy. In a society that values this ideology, the individual that cannot compete as successfully as others has a much lower income. A large gap occurs between rich and poor and, therefore, a low level of economic equality is evident. At the same time, American citizens have a high degree of political rights and freedoms.
Consider again the bar graph on page 315 in your textbook. Which countries have the highest grade of economic equality? Denmark, Sweden, Netherlands, and Austria. These countries favour a collectivist approach to their economies. This means that their governments are more involved in their economies and believe in providing more for their citizens' basic economic needs. In a society that values this ideology, the group (or government) helps its citizens with being more economically equal.
What grade does Canada get on this graph? Can you think of why that might be? Canada's economic system will be considered later.Economic Systems for Achieving Economic Equality
Earlier in this course you learned that every society's economic system is based on the same economic model. Review the economic model in the diagram below:
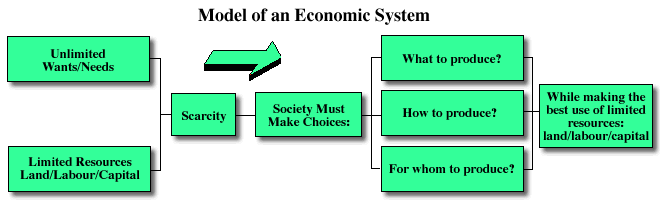
This diagram shows that the basic economic problem experienced by any economic system is the problem of scarcity. Scarcity occurs because a society's unlimited wants and needs are not matched by its limited resources of land, labour, and capital, also called the means of production. In other words, there is never enough to go around.
Due to scarcity, every society must determine how to make the best use of their limited resources or means of production by answering the three economic questions:
-
What to produce?
-
How to produce?
-
For whom to produce?
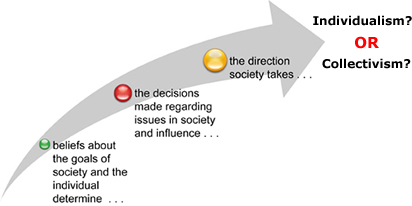
The model above demonstrates how a society organizes its economic system, but the direction the economic system takes is based on one of the following ideologies or perhaps a combination:
-
Individualism: Businesses and people make economic decisions about scarcity without government involvement, which benefits the common good.
-
Collectivism: Government makes economic decisions about scarcity for the common good of the collective group.
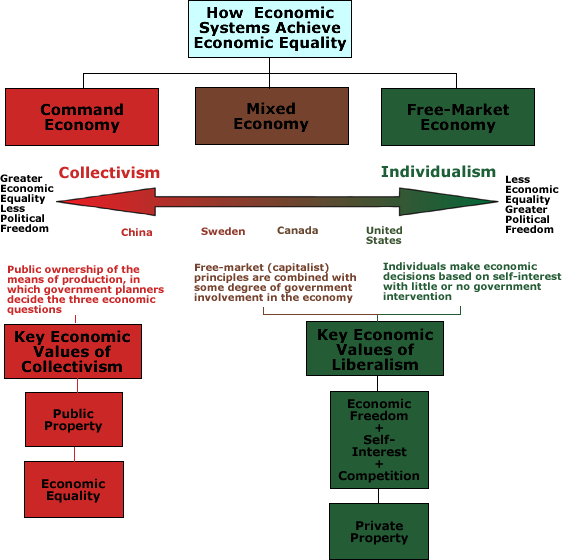
How do the various economic systems achieve economic equality?
This depends on the ideology of the society. There are a range of economic systems as a result, but most modern economic systems are of three types: command, free-market, and mixed.
Examine the following diagram to understand how each of these economic systems try to achieve economic equality.
-