Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.12. Lesson 2 Summary
Module 7: Absolute Value and Reciprocal Functions
Lesson 2 Summary

© MENZAGO/7241364/Fotolia
In this lesson you investigated the following questions:
- How do the properties of y = f(x) compare to those of
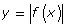 ?
?
- How can absolute value functions be written in piecewise notation?
Absolute value functions have the form ![]() , where f(x) is a function.
, where f(x) is a function.
In this lesson you learned how to graph absolute value functions. You discovered that you can do this by converting the y-values of all points located underneath the x-axis into positive values. The effect of doing this is to reflect all parts of the graph underneath the line y = 0 across the x-axis.
You also compared the properties of y = f(x) to those of ![]() . You found that the domain is the same for both functions, but that the range of the absolute value function depends on the range of the original function. Generally, the range of
. You found that the domain is the same for both functions, but that the range of the absolute value function depends on the range of the original function. Generally, the range of ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
Piecewise notation is a special way of expressing an absolute value function by describing each part of the function based on divisions at the critical points. You learned that, in general, ![]() .
.
In the next lesson you will investigate absolute value equations. You will learn how to determine the solutions of such equations both graphically and algebraically.