Section 2
1. Section 2
1.30. Explore 2
Section 2: Slope—Rate of Change
In the next example, proportions will be used to convert within and between SI and imperial units. As you have seen, the proportions you set up may vary but they can lead to the same answer.
Example
Bern Goosen is from South Africa. He has been disabled since birth due to cerebral palsy. Bern climbed Mount Kilimanjaro in October 2007 in a specially designed wheelchair.
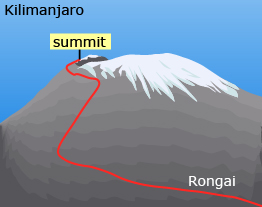
Goosen set a verified world wheelchair record for climbing to the summit of Mount Kilimanjaro. He took 6 days, 3 hours, and 20 minutes. Though the mountain is 5895 m tall, the actual distance that Bern climbed is 3885 m. He started the ascent from the mountain’s base, which left 2885 m to climb. This data is based on the route that he chose to use; other paths can be used. Note that the following graphic shows the Rongai Route that Bern used to climb the mountain.
- Determine the distance climbed in kilometres.
The actual distance climbed in kilometres can be determined by using a Climbing Table to set up a proportion based on the relationship 1 km = 1000 m.

- Find the number of miles Bern Goosen climbed based on the number of kilometres calculated in question 1. You can use the Mile Climbing Table for assistance.
You will use proportional reasoning starting from the relationship that 1 km = 0.6214 mi (rounded to the thousandths).