Lesson 3
1. Lesson 3
1.12. Explore 8
Module 7: Volume and Capacity
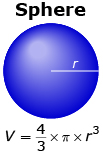
In Try This 3 you discovered that the volume of a sphere of radius r is given as ![]() . The formula may also be written as
. The formula may also be written as ![]() .
.
This formula can also be used to calculate capacity. Watch “Measurement 2 (Volume of a Sphere): Part 2” to review how the formula for the volume or capacity of a sphere relates to the formula for the volume of a cylinder.

iStockphoto/Thinkstock
Example
The diameter of a tennis ball is about 6.7 cm. To the nearest cubic centimetre, what is the volume of the tennis ball?
Solution

Hemera/Thinkstock
The diameter = 6.7 cm, so the radius, r, = 3.35 cm.
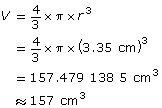
The volume of the tennis ball is approximately 157 cm3.
Example
For another example, turn to Page 154 of Mathworks 11 and read “Example 3.”
Self-Check 4
- The diameter of a cue ball is 2.25 in. What is the volume, in cubic inches, of a cue ball? Round your answer to one decimal place. Answer

AbleStock.com/Thinkstock
- A spherical tank that holds gas has an inner diameter of 8 m.

iStockphoto/Thinkstock
- What is the volume of gas the tank can hold, in cubic metres? Round to three decimal places. Answer
- Determine the capacity of the tank. If 1 m3 equals 1000 L, how many litres can the tank hold? Answer
- One United States gallon is equal to 3.785 L. To the nearest whole number, how many United States gallons does the tank hold? Answer
- What is the volume of gas the tank can hold, in cubic metres? Round to three decimal places. Answer
- Turn to page 158 of MathWorks 11. Answer question 5. Answer
You may now want to add the volume and capacity formulas for pyramids, cones, and spheres to your Formula Sheet.
