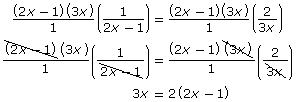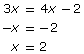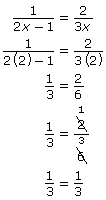Lesson 4
1. Lesson 4
1.7. Explore 3
Module 5: Rational Expressions
Try This 2 and Try This 3 focused on the steps involved in solving rational equations.
Step 1: Determine any non-permissible values.
Step 2: Multiply both sides of the equation by the LCD.
Step 3: Eliminate common factors.
Step 4: Solve the simplified equation.
Step 5: Check if the solutions are extraneous.
To confirm that you understand the process of solving simple rational equations, review the solution for ![]()
Step |
Your Work |
Step 1: Determine the non-permissible values. |
|
Step 2: Determine the LCD. |
LCD = (2x − 1)(3x) |
Step 3: Multiply by the LCD. |
|
Step 4: Simplify and solve the linear equation. |
|
Step 5: Check your solutions to see if they are extraneous.
Step 1 indicates that 2 is not a non‑permissible value.
Verify the solution by substituting 2 into the original equation and solving for each side. |
Since the LS = RS, the solution x = 2 is correct. |
Self-Check 1
Complete Solving Rational Equations Self-Check.