Module 1 Intro
1. Module 1 Intro
1.24. Page 3
Module 1—Energy Flow and the Cycling of Matter
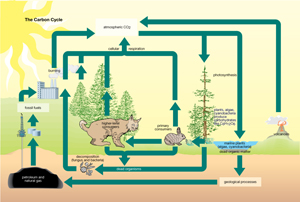
The Carbon Cycle
All life on Earth is based on molecules containing carbon. Atoms of carbon form the framework for proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and other molecules important to biological systems. The carbon cycle begins with producers taking in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. During photosynthesis, energy from the Sun is used by producers to convert carbon dioxide gas into energy-rich molecules of glucose to be used by living organisms as a source of food and energy. The simplified overall equation for photosynthesis is
Energy + 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) → C6H12O6(aq) + 6 O2(g)
Living organisms return carbon dioxide to the atmosphere by cellular respiration. The simplified overall equation for cellular respiration is
C6H12O6(aq) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) + Energy
The movement of carbon through the carbon cycle is highly affected by carbon being stored in a variety of reservoirs, including fossil fuels, animal fossils, and the vast reserves of calcium carbonate in the world’s oceans.
carbon sink: a system that removes more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases into the atmosphere
peat: deep layers of mosses and plant remains unable to completely decompose due to the lack of oxygen in water-saturated soil
Reservoirs of carbon are called carbon sinks. Boreal forest ecosystems are now recognized as significant carbon sinks not only due to the trees that live there, but also because of the accumulation of peat in these wetland ecosystems. Peat bogs in Alberta are called muskeg. Recent studies of peat bogs in Siberia have revealed that some of these bogs have been around since the last ice age, which makes them at least 10 000 years old.
These studies have also determined that peat bogs absorb huge amounts of carbon—this makes them among the world’s top carbon sinks. Unfortunately, if peat bogs are drained and decomposition is allowed to occur, the carbon stored there is released as carbon dioxide. These ecosystems then become a source of carbon instead of a sink.
 Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
Follow the movement of carbon as carbon dioxide or carbohydrate molecules through various possible pathways in the biosphere.
Bio-DiTRL http://bio-ditrl.sunsite.ualberta.ca/