Module 6 Intro
1. Module 6 Intro
1.12. Page 3
Module 6—The Motor System and Homeostasis
 Read
Read
It is important to note that injuries related to athletics are not the only potential problems for the muscular system. A number of muscle disorders, also known as myopathies, may occur that are unrelated to athletics. A summary of a number of common disorders and ailments is found on page 345 of the textbook. In addition, you can read or follow the links below in order to learn more about these and other common disorders.
Because “different types of muscles have different jobs,” many problems can affect muscles. Muscle disorders can cause weakness, pain, or even paralysis. There may be no known cause for a muscle disorder.
Some known causes include
- injury or overuse, such as sprains, strains or cramps, or tendonitis (A muscle strain is the stretching or tearing of muscle fibres. A muscle strain can be caused by sports, exercise, a sudden movement, or trying to lift something that is too heavy. Symptoms of a muscle strain include pain, tightness, swelling, tenderness, and an inability to move the muscle very well.)
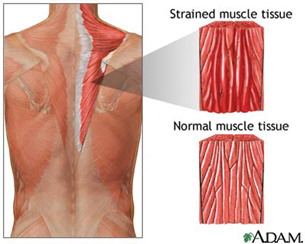
Courtesy National Institutes of Health
- genetics, such as muscular dystrophy (You can find more information on the Muscular Dystrophy Canada website.)
- some cancers (One source of more information is this article from the Mayo Clinic.)
- inflammation, such as myositis (The Myositis Association website will give you more information about myositis.)
- diseases of nerves that affect muscles
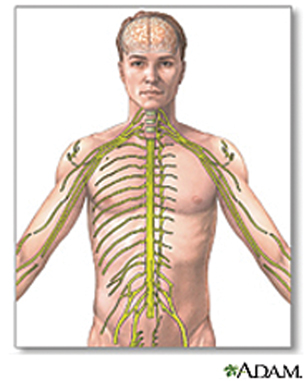
Courtesy National Library of Medicine
Neuromuscular Disorders
Neuromuscular disorders affect the nerves that control your voluntary muscles. Voluntary muscles are the ones you can control, such as in your arms and legs. Your nerve cells, also called neurons, send the messages that control these muscles. When the neurons become unhealthy or die, communication between your nervous system and muscles breaks down. As a result, your muscles weaken and waste away.
The weakness can lead to twitching, cramps, aches and pains, and joint and movement problems. Sometimes it also affects heart function and your ability to breathe.
Examples of neuromuscular disorders include
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- multiple sclerosis
- muscular dystrophy
- myasthenia gravis
- spinal muscular atrophy
Many neuromuscular diseases are genetic, which means they run in families or there is a mutation in a person’s genes. Sometimes, an immune system disorder can cause them. Most of these disorders have no cure. The goal of treatment is to improve symptoms, increase mobility, and lengthen life.
- infections
- certain medicines
 Try This
Try This
TR 2. Muscle Disorders
Research multiple sclerosis. Go to Lesson 2 Assignment to complete this activity.