Module 2
1. Module 2
1.18. Page 7
Module 2—The Endocrine System
 Reflect and Connect
Reflect and Connect
So, who is in charge of the endocrine system? Is it the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, or both? To review the connections between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland, watch the following segment of “The Hypothalamus and Pituitary: The Master Complex.” You may need to enter a username and password to access this video. Contact your teacher for this information.
- “Relationship Between the Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland”
Then, using what you have learned in this lesson about the hypothalamus, the posterior pituitary, and the anterior pituitary, decide which you think is the boss of the endocrine system. Provide as much evidence as possible to support your position. You may choose the hypothalamus, the posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary, or a combination of these structures. You may wish to discuss your ideas with your teacher or post your position and evidence on the discussion board for your peers to evaluate. Read at least two other students’ positions and discuss their evidence.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Complete the following multiple-choice questions, which will help assess your understanding of the concepts presented in this lesson. Discuss any questions that you do not understand with your teacher.
Use the following diagram to answer questions SC 16 and SC 17.

Adapted from Inquiry into Biology (Whitby, ON: McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2007), 445, fig. 13.12. Reproduced by permission.
SC 16. The structures labelled A and F, respectively, on this diagram are the
- hypothalamus and posterior pituitary
- hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
- anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary
- posterior pituitary and anterior pituitary
SC 17. The function of the structure labelled C on the diagram is to
- synthesize antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin
- stimulate release of ADH and oxytocin
- stimulate production of tropic hormones
- regulate the levels of ADH released into the blood

SC 18. Which endocrine gland shown on the diagram would be directly responsible for the development of dwarfism or gigantism in humans?
- G
- F
- B
- D
SC 19. Which of the following best explains the development of acromegaly in adults?
- increased production of TSH
- increased production of ACTH
- increased production of ADH
- increased production of hGH
Use the following feedback loop and information to answer questions SC 20 and SC 21.
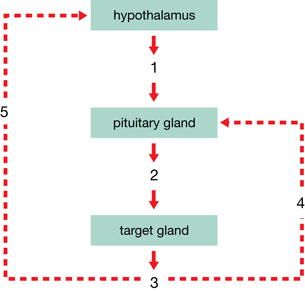
For this question, assume that the feedback loop shown is for a hormone primarily responsible for regulating the metabolic rate. The target cells for this hormone are all the cells of the body, which it stimulates to metabolize at a faster rate.
SC 20. Which row correctly identifies the hormones indicated by the numbers 1, 2, and 3 on the feedback loop?
Row |
Hormone 1 |
Hormone 2 |
Hormone 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
A. |
releasing hormone from hypothalamus |
thyroid stimulating hormone |
thyroxine |
B. |
releasing hormone from hypothalamus |
adrenocorticotropic hormone |
cortisol |
C. |
inhibiting hormone from hypothalamus |
human growth hormone |
growth factors |
D. |
inhibiting hormone from hypothalamus |
pancreas stimulating hormone |
insulin |
SC 21. The number 5 on the diagram would cause the release of which hormone?
- releasing hormone
- inhibiting hormone
- ACTH
- TSH
SC 22. The pituitary is often called the “master gland” because it
- receives impulses directly from the brain
- controls every other gland and organ in the body
- secretes hormones that control the functions of exocrine glands
- produces hormones that regulate the activities of other endocrine glands
SC 23. An abnormally large volume of urine may be produced after a person drinks alcoholic beverages. It is likely that ethyl alcohol affects normal secretion of
- antidiuretic hormone
- thyroxine
- cortisol
- aldosterone
Use the following information to answer question SC 24.
The following procedures and observations were used to determine the function of secretions from an animal organ suspected of being an endocrine gland.
|
SC 24. Based on these observations, the organ was the
- thyroid gland
- posterior pituitary
- hypothalamus
- anterior pituitary
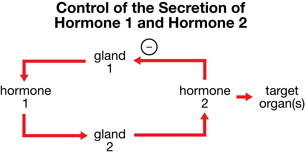
SC 25. If gland 1 is the pituitary gland, the row that identifies hormone 1, gland 2, and hormone 2 is
Row |
Hormone 1 |
Gland 2 |
Hormone 2 |
A. |
ACTH |
adrenal cortex |
adrenaline |
B. |
TSH |
thyroid |
thyroxine |
C. |
ACTH |
adrenal medulla |
cortisol |
D. |
ADH |
kidney |
aldosterone |
Use the following information to answer question SC 26.
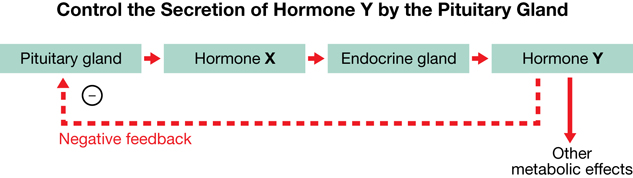
SC 26. Normally, inhibition of the pituitary gland would occur if the secretion of hormone X
- increased, causing a decrease in the secretion of hormone Y
- decreased, causing a decrease in the secretion of hormone Y
- increased, causing an increase in the secretion of hormone Y
- decreased, causing an increase in the secretion of hormone Y
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 16. B
SC 17. C
SC 18. C
SC 19. D
SC 20. A
SC 21. B
SC 22. D
SC 23. A
SC 24. D
SC 25. B
SC 26. C
 Reflect on the Big Picture
Reflect on the Big Picture
The endocrine system is self-regulating through its boss and through negative feedback mechanisms. You have had the opportunity to reflect on which part of the hypothalamus-pituitary complex you think is in charge. You have discussed your choice with your peers and teacher. But what happens when the boss of the endocrine system is not doing its job, as in Emily’s case? How are the regulatory pathways affected when tropic hormones are not functioning properly or aren’t present in adequate amounts?
In Lesson 3 you will examine Emily’s inability to regulate the stress hormones produced by the adrenal gland because her pituitary tumour causes too much ACTH to be secreted. In Lesson 4 you will examine the effects of her body not being able to regulate the thyroid hormone thyroxine because the tumour causes the undersecretion of TSH.
 Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment
Submit your completed Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment to your teacher for assessment.