Module 2
1. Module 2
1.38. Page 6
Module 2—The Endocrine System
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Apply your understanding of the concepts on the pancreas and its regulation of blood glucose by answering the multiple-choice and numerical-response questions that follow. Check your answers. If you do not understand any questions, consult your teacher.
Multiple-Choice Questions
SC 7. Which of the following rows correctly matches the endocrine gland to the hormone it secreted and to the effect caused by the hormone?
Row |
Endocrine Gland |
Hormone Secreted |
Target Cell/Organ |
A. |
thyroid gland |
thyroxine |
increases blood glucose |
B. |
pancreas |
insulin |
increases blood glucose |
C. |
pancreas |
glucagon |
increases blood glucose |
D. |
adrenal cortex |
epinephrine |
increases blood glucose |
SC 8. Which hormone is not correctly matched to the disorder or disease associated with it?
- insulin and diabetes mellitus
- aldosterone and diabetes insipidus
- thyroxine and goitre
- cortisol and depressed immune system
SC 9. Which of the following hormones does not affect the carbohydrate metabolism?
- human growth hormone
- epinephrine
- insulin
- ADH
SC 10. Which of the following endocrine glands does not produce a hormone that directly affects blood glucose levels?
- posterior pituitary
- pancreas
- adrenal glands
- thyroid gland
SC 11. Which of the following explains one of the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
- The treatment for Type 2 diabetes involves insulin injections, while Type 1 can usually be controlled by diet.
- Only Type 1 can result in complications such as kidney disease, reduced circulation, or stroke.
- Type 1 can be a result of lifestyle, and Type 2 is thought to be caused by a virus or other agent.
- People with Type 2 diabetes can produce insulin, but this insulin cannot be used. Type 1 diabetes results from lack of insulin production.
SC 12. Which pair consists of antagonistic hormones?
- thyroxine and calcitonin
- epinephrine and norepinephrine
- cortisol and epinephrine
- insulin and glucagon

SC 13. Which of the following rows correctly matches the endocrine gland labelled in the diagram to the hormone it produces?
Row |
Label on Diagram |
Endocrine Gland |
Hormone |
A. |
E |
adrenal gland |
cortisol and thyroxine |
B. |
A |
pituitary gland |
releasing hormone and ADH |
C. |
F |
pancreas |
insulin and glucagon |
D. |
C |
thyroid |
TSH and thyroxine |
SC 14. Which endocrine gland shown on this diagram would be directly responsible for the development of diabetes mellitus in humans?
- B
- D
- E
- F
SC 15. Symptoms resulting from low secretions of the hormones produced by the gland labelled F include
- high levels of sodium and sugar in the urine
- increased thirst and decreased urine production
- loss of weight and high levels of glucose in the urine
- obesity and increased risk of stroke
SC 16. The endocrine function of the pancreas was studied in Canada using dogs as experimental animals. The pancreatic cells with an endocrine function are
- islet cells
- C cells
- follicle cells
- interstitial cells
Use the following diagram to answer question SC 17.
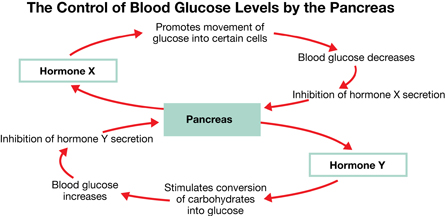
SC 17. Hormones X and Y, respectively, are
- insulin and glucagon
- glucagon and insulin
- insulin and epinephrine
- epinephrine and insulin
Use the following information to answer questions SC 18 and SC 19.
A Treatment for Pancreatitis
Surgical removal of the pancreas is a procedure that doctors use to relieve the pain of patients suffering from chronic pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Unfortunately, the surgery causes the onset of diabetes mellitus and other complications in these patients. In a recent study involving five individuals who had undergone this treatment, islet cells from the removed pancreas were infused (transplanted) back into the liver of each patient. This procedure effectively eliminated the occurrence of diabetes in these patients. |
SC 18. Blood glucose levels are kept relatively constant by a negative feedback mechanism. The islet cells are part of this mechanism. The role of these cells is to secrete
- glucagon to raise blood glucose levels, and insulin to lower blood glucose levels
- glucagon to lower blood glucose levels, and insulin to raise blood glucose levels
- glucagon and insulin, both of which lower blood glucose levels
- glucagon and insulin, both of which raise blood glucose levels
SC 19. Patients who participated in this study no longer have a pancreas. To maintain normal body functions in these patients, the infusion of islet cells would have to be accompanied by a daily intake of
- glycogen to stimulate liver function
- hormones to promote glycogen release from the liver
- digestive enzymes into the blood to maintain nutrient levels
- digestive enzymes to replace those produced by the pancreas
Numerical-Response Questions
Use the following information to answer question SC 20.
Responses Stimulated by Hormones
|
SC 20. Identify the response, as numbered above, that would be stimulated by each of the hormones given below.
Response:
______ ______ ______ ______
Hormone: Insulin Cortisol Glucagon hGH
Use the following information to answer question SC 21.
Some Endocrine Glands and Hormones
|
SC 21. To complete this statement, select the number of the gland or hormone from the information above that best completes each blank.
The hormones of the _____ act antagonistically to regulate blood glucose levels. The beta cells of the islets of Langerhans secrete ____, which lowers blood glucose levels. The alpha cells secrete _____, which raises blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes causes hyperglycemia because the secreting cells have degenerated. Type 2 diabetes tends to develop gradually, often because the _____ receptors on the body’s cells stop responding to this hormone.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 7. C
SC 8. B
SC 9. D
SC 10. A
SC 11. D
SC 12. D
SC 13. C
SC 14. D
SC 15. C
SC 16. A
SC 17. A
SC 18. A
SC 19. D
SC 20. 5, 4, 6, 2 (in that order)
SC 21. 4, 2, 5, 2 (in that order)