Module 6
1. Module 6
1.5. Page 3
Module 6—Mendelian Genetics: The Transmission of Traits to the Next Generation
 Read
Read
trait: a characteristic
pure: an individual with both alleles for a trait being dominant, or recessive
contrasting characteristic: a trait that has two alleles that are expressed in a different way (e.g., the trait for height in pea plants can have the contrasting characteristics of tall or short)
factor: the term used by Gregor Mendel to explain inheritance of a trait; today we use the term gene
law of segregation: the two genes that an organism has for each trait are separated during meiosis so that only one gene can enter a gamete; explains why body cells are diploid, but gametes are haploid
The video “Classical Genetics and Monohybrid Crosses” presented how Mendel discovered two variations of traits for each characteristic that he studied. One trait is dominant over the other. The evidence for this was discovered when he crossed two pure plants with contrasting characteristics, such as Tall (T) or short (t) plants. The first generation plants, or F1, all showed a Tall phenotype. The short trait seemed to disappear. However, when these plants self fertilized, their offspring, the F2, were a mix of tall and short plants. Read the section “Dominant and Recessive Genes” in your text on page 588 for a better understanding of this mode of inheritance.
Mendel proposed that each trait was controlled by factors. We now call these factors genes, and the different forms of genes are termed alleles. Each plant will have two alleles present for each characteristic, and will pass down only one of these alleles when they create gamete cells (sperm or egg). The combination of the two alleles received by a gamete is random, and this type of separation is known as Mendel’s first law: the law of segregation. For a greater understanding of this law, please read “The Law of Segregation” in your text on page 589. Summarize this law in words or a diagram and file in your course folder.
 Try This
Try This
TR 18. Complete the Terminology Drag and Drop activity.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
To check your understanding, complete the following questions.
SC 1.
- Separate the two chromosomes by meiosis.

- What type of cell is formed as a result of meiosis?
- What term is used to describe “T” and “t”?
- Which of Mendel’s Laws does the above example illustrate?
SC 2. Use the appropriate term to describe each of the following items: genotype, phenotype, segregation.
Blue eyes
a. _______________
bb
b. ________________
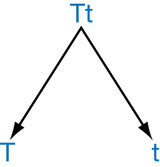
c. _________________
SC 3. Indicate whether each of the following is a trait or a characteristic.
- wrinkled seed
- curly hair
- pod colour
- plant height
SC 4. How many different types of gametes would an individual with the following genotypes produce? (Hint: Each gamete will contain only one from each letter pair.)
- AABBCC
- AaBbCc
- AaBbCC
SC 5. What are the gamete types produced by an individual with genotype WWTtPp?
SC 6. What evidence is there for Mendel’s principle of dominance?
SC 7. Which term identifies or describes the following genotypes?
- Rr/Pp –
- RR/PP –
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 1.
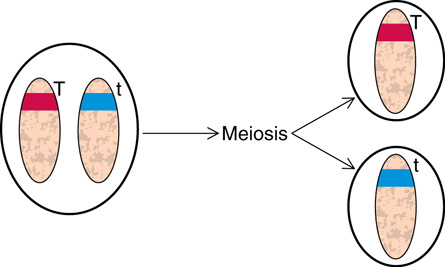
- the cells created by meiosis are called gametes
- the “T” and “t” are known as alleles, with “T” being dominant and “t” being recessive
- The Law of Segregation
SC 2. a. phenotype
b. genotype
c. segregation
SC 3.
- trait
- trait
- characteristic
- characteristic
SC 4.
- 1
- 8
- 4
SC 5. WTP, WTp, WtP, Wtp – four unique gametes
SC 6. the reappearance of the recessive trait in the F2
SC 7. a. heterozygous
b. homozygous or true breeding.