Module 6
1. Module 6
1.20. Page 3
Module 6—Mendelian Genetics: The Transmission of Traits to the Next Generation
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Answer the following questions to check your understanding of the material in this lesson.
SC 1. In pepper plants, green (G) fruit colour is dominant to red (g) fruit colour, and round (R) fruit shape is dominant to square (r) fruit shape. These two genes are located on different chromosomes.
- What gamete types will be produced by a heterozygous green, round plant?
- If two such heterozygous plants are crossed, what genotypes and phenotypes will be seen in the offspring, and in what proportions?
SC 2. In watermelons, the genes for green colour and for short shape are dominant over the alleles for striped colour and for long shape. Suppose a plant with long, striped fruit is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for green colour and homozygous for short shape. What is the phenotype of their offspring? (Be sure to show all your work).
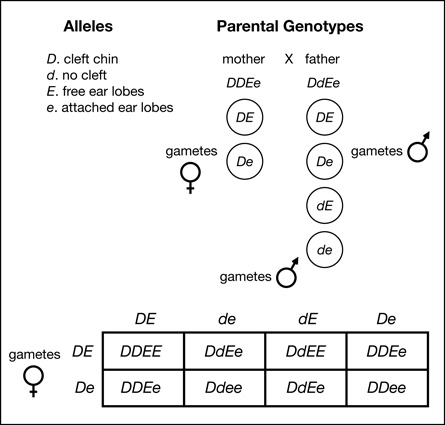
SC 3. In humans, a cleft chin is due to a dominant allele (D), while the recessive allele (d) produces no cleft. Most people have free earlobes due to a dominant allele (E), and a person with attached ear lobes has two recessive alleles (e). If a mother is homozygous for cleft chin and heterozygous for free earlobes, and the father is heterozygous for both traits, determine the following:
- What is the probability that their baby will have the following combinations?
- a cleft chin and attached ear lobes
- a cleft chin and free ear lobes
- no cleft chin and free ear lobes
- no cleft chin and attached ear lobes
- Draw a Punnett square to support your answer.
SC 4. The allele for black coat colour (B) is dominant over the allele for white coat colour (b) in dogs. The allele for short hair (S) is dominant over the allele for long hair (s). The phenotypes of offspring from several crosses are given below.
Cross |
Parental Phenotypes |
Phenotypes of Offspring |
|||
Black, Short |
Black, Long |
White, Short |
White, Long |
||
1 |
black, short x black, long |
16 |
15 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
white, short x white, short |
0 |
0 |
27 |
8 |
3 |
black, short x black, long |
6 |
5 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
black, long x black, long |
0 |
31 |
0 |
10 |
Answer the following questions using the information provided in the table above.
- What are the genotypes for parents of each of the four crosses?
- If the black coat colour and long hair offspring from Cross 3 is crossed with the black coat colour and short hair offspring from Cross 1 (assume both parents are BB), what proportion of the offspring will have black, short hair? Is it possible to have offspring with white, long hair from this cross?
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 1.
- The green round plant will produce GR, Gr, gR, and gr gametes in equal proportion since the genes are unlinked.
- This will give
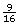 green round,
green round, 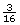 green square,
green square, 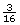 red round, and
red round, and 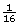 red square phenotypes; the genotypes are given in the Punnett square below.
red square phenotypes; the genotypes are given in the Punnett square below.
GR Gr gR gr GR GR GR GR Gr GR gR GR gr Gr Gr GR Gr Gr Gr gR Gr gr gR gR GR gR Gr gR gR gR gr gr gr GR gr Gr gr gR gr gr
SC 2.
Allele assignment: G = green, g = stripped, S = short, s = long.
Parents: ggss x GgSS
Gametes: [gs] x [GS], [gS]
Offspring: GgSs, ggSs
Phenotype: 50% green short : 50% striped short
SC 3. Parents: DDEe x DdEe
Gametes: [DE], [De] x [DE], [De], [dE], [de]
a.
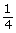
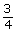
- 0
- 0
b.
SC 4.
- Cross 1: BBSs x BBss Cross 2: bbSs x bbSs
Cross 3: BbSs x Bbss Cross 4: Bbss x Bbss
- Offspring with black, short hair:
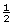 or 50%
or 50%
It is not possible to have offspring with white, long hair since the only colour allele present is B.