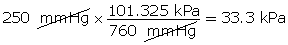Module 3 Intro
1. Module 3 Intro
1.4. Page 2
Module 3—Behaviour of Gases
 Explore
Explore
 Read
Read
Gases exert a pressure, a force on surfaces they come in contact with. Atmospheric pressure is a measurement you often hear about since changes in pressure often bring a change to local weather.
To learn more about pressure and how the pressure exerted by a gas is measured, read “Pressure” on pages 148 and 149 in your textbook.
You may wish to prepare a list of the most important information in this reading. Compare your list with these summary notes on pressure. Save a copy of your notes or add the summary notes to your course folder for reference.
 Read
Read
You can see that a variety of units can be used to communicate a measurement of the pressure of a gas. In some situations it is necessary to convert between units. Equivalencies between the units are shown in the summary notes and in “Table 2: SI and Non-SI Units of Pressure” on page 149 of your textbook.
Carefully work through “COMMUNICATION example 1” on page 150 and the following examples.
Conversions between units may involve one set, or multiple equivalencies. You will need to use the equivalencies in your summary table.
A convenient method used in converting between units is to arrange the equivalencies into a fraction where the numerator and denominator are equal, but they are values in two different units. The numerator of the fraction should have the units that you want to convert to, and the denominator of your fraction should have the units you want to convert from. This arrangement will allow the unwanted units to cancel.
Example 1
- Convert 3.21 atm into units of kPa.
(Hint: 1 atm = 101.325 kPa)
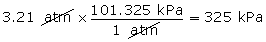
- Convert 0.78 bars into units of kPa.
(Hint: 1 bar = 100 kPa)
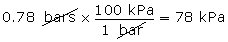
- Convert 670 mm Hg into units of torr.
(Hint: 1 torr = 1 mm Hg)
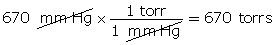
- Convert 167 kPa into units of atm.
(Hint: 1 atm = 101.325 kPa)
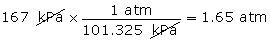
Equivalencies can be written between units shown on the table that are not already listed. For example, what is the equivalency between kPa and mm Hg? After you have command of these equivalencies, you can complete other unit conversions.
Example 2
- Convert 250 mmHg into units of kPa.
(Hint: 760 mm Hg = 1 atm = 101.325 kPa)