Module 5
1. Module 5
1.27. Page 4
Module 5—Wave Theory of Light
 Reflect and Connect
Reflect and Connect

© Scott Hales/shutterstock
Myopia, commonly known as near-sightedness or short-sightedness, occurs when the light entering the eye is refracted too sharply. This causes the image to form in front of the retina. To correct this type of disorder, a diverging lens can be placed in front of the eye to alter the light-ray paths so that they converge on the surface of the retina and restore clear vision.

The diverging lens is identified as a negative prescription, since it has a negative, virtual focal length. The amount of refraction caused by the lens is identified numerically using a unit called diopters, which is the reciprocal of the lens’s focal length. For example, a −2 lens prescription is a diverging lens with a virtual focal length of ![]() metre. A −3 lens will refract light to a greater extent than the −2 lens, since it has a shorter focal length of
metre. A −3 lens will refract light to a greater extent than the −2 lens, since it has a shorter focal length of ![]() metre. The strength of the lens is related to both the refractive index of the material from which it is made and the curvature of the surface. Different prescriptions are manufactured by altering either the lens material or its curvature.
metre. The strength of the lens is related to both the refractive index of the material from which it is made and the curvature of the surface. Different prescriptions are manufactured by altering either the lens material or its curvature.
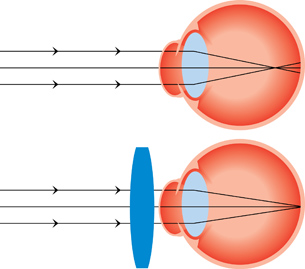
Hyperopia, or far-sightedness, occurs when light is not refracted enough to converge on the retina. To correct this condition, a converging lens is used to refract the light farther, effectively moving the image formation forward so that the light occurs on the retina tissue.
Far-sightedness is treated with positive diopter prescriptions. For example, a +3 lens has a real focal length of ![]() m. Reading glasses are a good example of a positive prescription lens that many people use to view objects up close, such as the text in books.
m. Reading glasses are a good example of a positive prescription lens that many people use to view objects up close, such as the text in books.
In a general sense, eyeglasses are an extension of the optical system of the human eye and are capable of causing specific amounts of refraction to remedy imperfections in the lens or cornea of the user. The thin lens equation and ray diagrams are used to understand and predict image formation in such applications.
 Module 5: Lesson 5 Assignment
Module 5: Lesson 5 Assignment
Remember to submit the Module 5: Lesson 5 Assignment to your teacher.