Lesson One - Groups and Organizations
1.2 Groups and Networks
Making Connections: Research
Conforming to Expectations
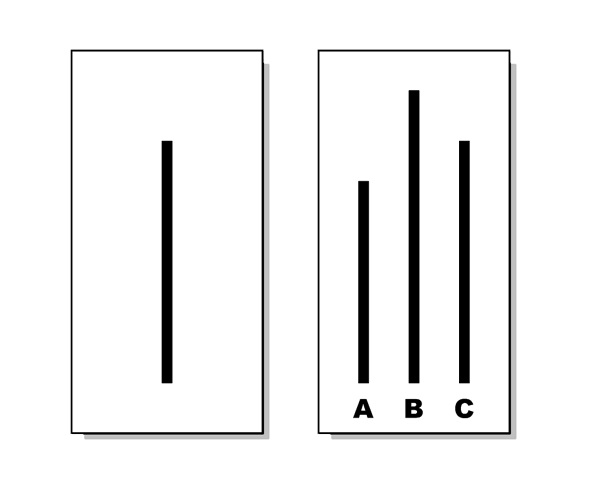
Figure 6.9. In the Asch conformity experiments a subject had to determine which of the three lines on the left matched the length of the line on the right. (Photo courtesy of Nyenyec/Wikimedia Commons). 
Psychologist Solomon Asch (1907–1996) conducted experiments that illustrated how great the pressure to conform is, specifically within a small group (1956). In 1951, he sat a small group of eight people around a table. Only one of the people sitting there was the true experimental subject; the rest were actors or associates of the experimenter. However, the subject was led to believe that the others were all, like him, people brought in for an experiment in visual judgments. The group was shown two cards, the first card with a single vertical line, and the second card with three vertical lines differing in length. The experimenter polled the group, asking each participant one at a time which line on the second card matched up with the line on the first card.
However, this was not really a test of visual judgment. Rather, it was Asch’s study on the pressures of conformity. He was curious to see what the effect of multiple wrong answers would be on the subject, who presumably was able to tell which lines matched. In order to test this, Asch had each planted respondent answer in a specific way. The subject was seated in such a way that he had to hear almost everyone else’s answers before it was his turn. Sometimes the non-subject members would unanimously choose an answer that was clearly wrong.
So what was the conclusion? Asch found that 37 out of 50 test subjects responded with an “obviously erroneous” answer at least once. When faced by a unanimous wrong answer from the rest of the group, the subject conformed to a mean of four of the staged answers. Asch revised the study and repeated it, wherein the subject still heard the staged wrong answers, but was allowed to write down his answer rather than speak it aloud. In this version, the number of examples of conformity—giving an incorrect answer so as not to contradict the group—fell by two-thirds. He also found that group size had an impact on how much pressure the subject felt to conform.
The results showed that speaking up when only one other person gave an erroneous answer was far more common than when five or six people defended the incorrect position. Finally, Asch discovered that people were far more likely to give the correct answer in the face of near-unanimous consent if they had a single ally. If even one person in the group also dissented, the subject conformed only a quarter as often. Clearly, it was easier to be a minority of two than a minority of one.
Asch concluded that there are two main causes for conformity: people want to be liked by the group or they believe the group is better informed than they are. He found his study results disturbing. To him, they revealed that intelligent, well-educated people would, with very little coaxing, go along with an untruth. He believed this result highlighted real problems with the education system and values in our society (Asch 1956).
What would you do in Asch’s experiment? Would you speak up? What would help you speak up and what would discourage you?