Project 1
| Site: | MoodleHUB.ca 🍁 |
| Course: | INF1030 |
| Book: | Project 1 |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 26 December 2025, 9:35 AM |
Description
Created by IMSreader
1. Project 1
Project 1: Workstation Routines and Management

© Marcel Mooij/shutterstock
Have you ever actually read the software licensing terms of the software you run on your computer? Have you ever scratched or damaged your CDs or DVDs, contracted a computer virus, or spilled a drink on your keyboard? Have you ever worked or played on a computer for so long that your muscles burned in your back or in your neck or felt your eyes sting from staring at the screen? Or have your hands ever cramped up or felt tingly after keyboarding, gaming, or instant messaging?
It’s easy to become so absorbed when working at the computer that you forget how long you have been sitting in one position, overstressing your muscles, and straining your eyes.

© Marcel Mooij/shutterstock
Working with computers can be problematic if you don't follow good routines and practices that protect both your health and your equipment. However, making good workstation routines a habit will help you minimize or prevent damage to equipment, loss of personal work, and injuries associated with using a computer and help increase your productivity, personal satisfaction, and sense of accomplishment.
In this project you will discover and practise appropriate workstation routines, setting personal goals for yourself to be aware and to practise ergonomic routines each time you sit at a computer.
What is required to complete this project?
To complete this project you will need the following:
- Workstation Routines Rubric
- Internet access
- camera (film, digital, or cell phone) or web cam
What do I already know?
You may have already completed another CTS module and have learned about and have practised good workstation routines. If this is the case, now is a good time to review the Workstation Routines Rubric and set new goals for improving your workstation routines in different areas. Check with your teacher about how to proceed for this section. 
repetitive strain injury: overuse of the muscles through repeated movements that put stress on certain body parts, such as wrists or elbows
carpal tunnel syndrome: a medical condition in which the median nerve is compressed at the wrist causing pain, weakness, or numbness in the hand or wrist that can radiate up the arm
You may have seen people wear braces on their wrists for repetitive strain injury or carpal tunnel syndrome, and you probably know that people can develop injuries from poor body posture, improper keyboard and mouse techniques, and prolonged intervals in front of a computer. Think about an experience where you spent an extended amount of time doing the same task, like playing a video game or shovelling the snow. The repetitive movement of one part of your body can cause strain and discomfort.
What do I need to do?
- learn about workstation ergonomics and computer safety and security
- analyze your workstation and make necessary improvements
- apply and practise the skills
- self-evaluate your workstation position and routines
1.1. Page 2
Project 1: Workstation Routines and Management
Time to Work
This project will take approximately 1.5 hours. The information from this project should be practised throughout the course.
Before you begin, print and review a copy of the Workstation Routines Rubric.
For this course you will need to set up a central location to store documents you create. Go to the Project 1 Instructional Videos in the Toolkit and watch the demonstration “Creating a New Folder and Subfolders” to learn how to create folders for INF1030: Word Processing 1. Check with your teacher as to where you will be saving your files.
Create a folder called “INF1030 WP1.” Then create the following subfolders within the INF1030 WP1 folder:
- Workstation Routines
- Basic Competencies
- Letters
- Graphics
- Reports
- Tables
- Final Project
Now, it’s time to begin the project.
Step 1: Create a new word processing document. Save the file in the Project 1 folder and name it “Ergonomics.”
To review how to create, open, and save a word processing file, go to the Project 1 Instructional Videos in the Toolkit and watch the following demonstrations:
- Creating and Saving a File
- Saving and Opening a Document
Step 2: Add a header and/or footer to your file that include your name, assignment name, and date.
Go to the Project 1 Instructional Videos in the Toolkit and watch the demonstration “Headers and Footers” to review formatting headers and footers in Microsoft Word® 2007.
- Using the Internet, the glossary, or a dictionary, look up the word ergonomics and write a definition in your own words in your word processing document. Save your Ergonomics document.
Step 3: Now that you know what ergonomics is, take some time to read the information in the Workstation Ergonomics document. Do you have anything to add to your definition of ergonomics? If so, open your document and make the changes. Then resave the document.
Step 4: Watch the "Ergonomics" video.

© Juriah Mosin/shutterstock
Step 5: Study the following diagram on arranging a work surface. It is important to ensure that you, too, have a clean, well-organized area in which to work.
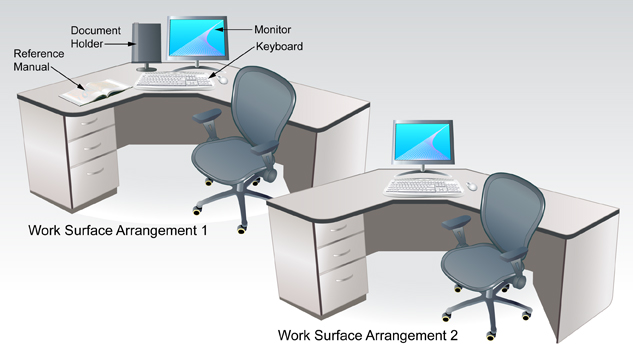
Adapted from: © sahua d/shutterstock. book: © Dan Gerber/shutterstock
This is your opportunity to improve your computer workstation. Using the information and routines you have been given, make appropriate adjustments to your furniture, equipment, and resources. If you have access to a camera, take before and after pictures.
Answer the following questions in your Ergonomics document.
- How many changes did you make?
- What corrections were you not able to make because of inadequate furniture, accessories, or lab restrictions?
- What does practising good ergonomics and setting up an efficient, safe, and organized work station mean to you?
- How can making this practice a habit help you in the long run both personally and as you enter into the workforce?
Resave your document.

© Juriah Mosin/shutterstock
Remember: Make stretching a part of your routine. Practise the exercises you have been shown every 30 min. Be sure to exercise your shoulders, back, neck, wrists, fingers, and arms.
Step 6: Read the document Workstation Security for information regarding hardware and software security and keeping your personal work secure.
- Answer the following questions. You can use Internet search terms to perform some research on these topics as well.
- List three ways to protect your equipment or secure your work.
- List three ways you can protect your computer from viruses.
- In the Ergonomics document you created, comment on your areas of strength and weakness. Set a goal to improve one or two areas you identified as needing improvement. Here are a few examples of possible goals:
- I remember to stretch every 30 min to help reduce muscle fatigue.
- I save files frequently as I work and backup important files regularly.
Step 7: Using the Workstations Routine Rubric, complete a self-evaluation to identify areas that you may need to work on throughout the module. Revisit the Workstation Routine Rubric periodically throughout the course and self-evaluate your progress in making appropriate workstation routines a daily habit.
1.2. Page 3
Project 1: Workstation Routines and Management
Checking Your Work

© Marc Dietrich/shutterstock
Practising good workstation positions, routines, and security quickly becomes a habit when you practise these skills and techniques every time you sit at a computer. Using good routines and practices will make you more productive and reduce the likelihood of injury; protecting your equipment and personal work from loss or damage will also save you time, money, and frustration.
Remember, continue to self-evaluate and reflect on your workstation management and correct routines to obtain optimum health, safety, and security. You will be evaluated on your workstation management by your teacher at the end of the course.
1.3. Project 1 Summary
Project 1: Workstation Routines and Management
Project 1 Summary
Now that you have completed this project, you should be able to recognize and apply efficient workstation positions, routines, and security practices to make working with a computer a more enjoyable, healthy, safe, and productive experience.