Lesson 2: Using Measuring Instruments
| Site: | MoodleHUB.ca 🍁 |
| Course: | Mathematics 10C |
| Book: | Lesson 2: Using Measuring Instruments |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 19 December 2025, 5:23 AM |
Focus

In Lesson 1 you learned how to estimate SI (metric) and imperial measurements using referents. Estimation is a very important skill that helps you to plan ahead and also to check that your results are reasonable. You will continue to build on this skill in Lesson 2.
Perhaps as part of your unit project, you need to create a cylindrical shape, a very small opening, or a quarter pipe. How can you figure out the required measurements? In what units will you measure your object, and with what instrument?
In this lesson you will expand on your ability to measure while you think about how you can measure large, small, or curved objects.
Outcomes
At the end of this lesson, you will be able to
- justify the choice of units used for determining a measurement in a problem-solving context
- solve problems that involve linear measure, using instruments such as rulers, calipers, or tape measures
- describe and explain a personal strategy used to determine a linear measurement; e.g., the circumference of a bottle, the length of a curve, or the perimeter of the base of an irregular 3-D object
Lesson Questions
- How do you choose the appropriate techniques, instruments, and formula to describe the dimensions of an object?
- How can you measure the dimensions of objects of irregular shape or size?
![]() Lesson Completion and Assessment
Lesson Completion and Assessment
As you work through each lesson, complete all the questions and learning activities in your binder using paper and pencil, clearly labeling your work (they refer to this as your course folder). These include the Are you Ready, Try This, Share and Self Check questions. Check your work if answers are provided. Remember that these questions provide you with the practice and feedback that you need to successfully complete this course.
Once you have completed all of the learning activities, take the Lesson Quiz. This is the assessment for each lesson and is located under the Assess tab or using the Quizzes link under the Activities block.
** Note – Share questions may have to be done on your own depending on your learning situation**
Launch
Complete these questions in your course folder (binder). If you are experiencing difficulty, you may want to use the information and the multimedia in the Refresher section to clarify concepts before completing these exercises.
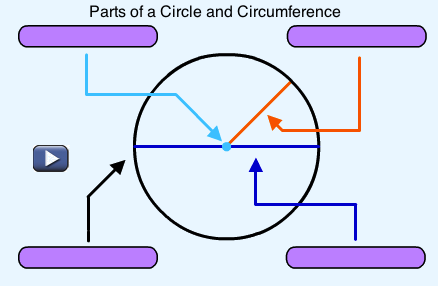
1. What is meant by the circumference of a circle?
2. The formula for the circumference of a circle is C = πd. Use the formula to calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 12 mm. Report your answer to the nearest tenth of a millimetre.3. Put the following metric units in order from smallest to largest:
km m mm cm
4. Put the following imperial units in order from smallest to largest:yard inch mile foot
5. What is meant by the perimeter of a polygon?6. Determine the perimeter of the shapes below:
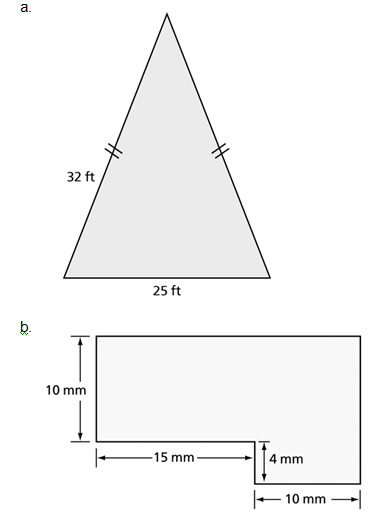
Once you have completed these exercises to the best of your ability, check your work using the link provided.
If you feel comfortable with the concepts covered in the questions, move forward to Discover. If you experienced difficulties, use the resources in Refresher to review these important concepts before continuing through the lesson or contact your teacher.
![]() Refresher
Refresher
Below you will find links to some video clips that may help refresh your memory. These interactive pieces will help you to answer the following questions:
-
How do I determine the circumference of a circle?
-
How do I calculate the perimeter of a polygon or an enclosed shape with straight sides?
The multimedia lesson titled “Parts of a Circle and Circumference” reviews the parts of a circle and explores the relationships between the diameter, radius, and circumference of a circle. The value of pi is discussed, and the lesson includes a game and practical math problems that require using the formula for the circumference of a circle. (You may need to log in using username LA53 and password 4487).
The LearnAlberta resource from the Mathematics Glossary defines the term perimeter.
Go to “Perimeter”.
It contains an animation to illustrate the definition. Try “Example” at the bottom of the web page.
Materials
-
measuring tapes and rulers
-
30-cm long string
-
3-D modelling program (e.g., Google SketchUp)
Discover
![]() Try This
Try This
Complete the following in your course folder (binder).
TT1: First, draw a circle on a piece of paper by tracing around the bottom of a mug or around a CD.
Next, use a tape measure or a ruler to measure the diameter of the circle.
Now use a formula to determine the circumference of the circle. (Hint: You reviewed this formula in the Launch section.)
![]() Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
Now that you have tried to measure the diameter of a circle that you have drawn, watch the video clip titled “Measuring a Non-Linear Path.”
------------------------------------------------------
![]() Try This
Try This
Complete the following in your course folder (binder).
TT2: Use the technique shown in the video to measure the circumference of the circle that you drew in TT 1. Compare your answer with the one obtained in TT 1. Which method do you think is more accurate? Why?
TT3: Describe one advantage for each method.
TT4: Describe one drawback for each method.
TT5: Which method would you use to measure the circumference of a tree trunk? Why?
TT6: How could you measure the diameter of a tree trunk without chopping the tree down?
Use the link below to check your answers from Try This 1 - 6.
Explore

trundle wheel: © Bart Coenders/iStockphoto; Vernier caliper: © Adem Demir/shutterstock
Glossary Terms
In this course you will often come across math-related words that may be unfamiliar to you. In Lesson 1 you started a list of glossary terms.
Add the following terms to your “Glossary Terms” page:
-
circumference
-
diameter
-
dimensions
-
irregular shape
-
trundle wheel
-
vernier caliper
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You have the SI (metric) units and the imperial units estimated as body referents, your ruler, an online caliper, and a tape measure, so where do you start? Well, it depends on what you are trying to measure and how accurate a measurement you require.
In construction, sometimes you need a sledge hammer and sometimes you need a ball-peen hammer. The same idea applies in measurement: different instruments provide different scales. You will investigate measurement instruments and their usefulness.
![]() Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
Trundle Wheel
Have you ever had to measure a distance that is too long for a tape measure or a metre-stick? Maybe you want to know how far it is to the end of your street. Instead of using a stretched-out tape measure over and over, you can use a trundle wheel.
The video titled “Trundle Wheel” will show you how.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vernier Caliper
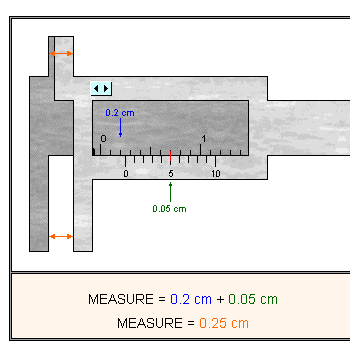
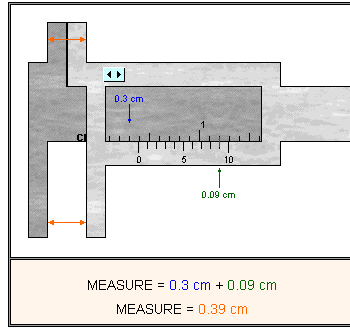
A plumber may have to measure the diameter of a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pipe in order to know if the pipe will be suitable for a repair job. One way to obtain the proper measurement is by using a vernier caliper. A Vernier Caliper allows for very precise measurements for items that are difficult to measure using other tools (circular items, very small items).
Generally, to read a Vernier Caliper, we use the top scale ( the main scale) for the first decimal and the bottom scale for the second decimals. Here are some steps for using a vernier caliper:
1. For the tenths digit, look to see where the 0 on the bottom scale is located in reference to the top scale. Choose the number that is just before where the 0 is located.
2. Now look to the bottom scale and see where the lines match up perfectly for the first time. This gives the hundredth digit.
Here are a few solved examples for you to look through.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SI Ruler
Click below to watch how to measure using an SI ( Metric) ruler.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Imperial Ruler
Use the link below to watch how to use an Imperial Ruler for measuring.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
![]() Try This
Try This
Complete the following in your course folder (binder).
TT 7. Using the provided imperial ruler, how long does the red line measure?
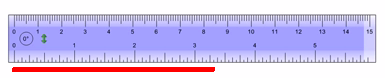
TT 8. Use a piece of string and a ruler or a tape measure to measure the circumference of a round or cylindrical object. Some objects you may consider measuring include a glass, a basketball, a can of soup, or an orange. Is this technique an effective way to measure the circumference of objects that you found? Explain.
TT 9. If you have access to a trundle wheel, use the wheel to measure the perimeter of a room in your immediate environment. Is there a better way to measure the perimeter of a room? Explain.
Use the link below to check your answers to Try This 7 - 9.
Whenever you have been required to measure something in this lesson, you have also been told which measurement instrument to use. However, as you work on projects in your home, you will need to decide for yourself what are the most appropriate instruments and units to use.
When deciding which measurement instrument to use, you will need to consider the following.
|
Question |
Considerations |
|
What measurement instruments do I have available? |
You may have limited options. You may have to borrow or purchase the right instrument. |
|
Am I measuring something that is short or long? |
You likely won’t want to measure the length of a hallway with a ruler or the thickness of a dime with a trundle wheel. |
|
Is the scale on the measurement instrument big enough? |
You can’t measure the diameter of a beach ball using a vernier caliper! |
|
Are the divisions on the scale small enough to give a precise measurement? |
How precise you want the measurement to be may determine which instrument you need to use. |
You will also need to decide what unit of measurement to use when measuring an object. Some questions you will need to answer include these ones.
|
Question |
Considerations |
|
Do I need the measurement to be in SI units or imperial units? |
You may need to report measurements in SI units if previous measurements were also in SI units. |
|
Am I measuring something that is short or long? |
If something is long, like the length of a building, you would likely avoid using inches or millimetres as the units of measure. |
|
What measurement instrument am I using? |
The instrument that you use will have a certain scale; |
|
Which units will give me a reasonable answer? |
The length of a swimming pool could be reported as 50 000 mm, 5000 cm, 50 m, or 0.05 km. The most appropriate example is 50 m. |
![]() Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1. Match the following scenarios with the correct measurement instruments.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SC 2. You have used your caliper to determine that a Canadian dime has a thickness of 1.22 mm and a diameter of 18.03 mm.
- Determine the circumference of this dime.
- How many dimes can fit into a container that has the following dimensions?

Connect
Complete the lesson quiz posted under the Assess tab or using the Quizzes link in the Activities block. Also ensure your work in your binder (course folder) is complete.
![]() Project Connection **NOT ASSIGNED**
Project Connection **NOT ASSIGNED**
Think about the special place that is the basis for your Unit 1 Project, and complete the Lesson 2 portion.
![]() Going Beyond
Going Beyond
Because some things are so small, they are impossible to detect with the naked eye. Take a look at the multimedia piece titled “Cell Size and Scale1” to get a feeling for how small some objects and organisms are.
How would you measure the dimensions of something so small that you cannot see it with the naked eye? For example, how can you measure the width of a plant or animal cell? In this case, you would have to measure the item under a microscope. Use an Internet search engine to discover the steps for measuring the dimensions of a microscopic object or organism.
1Genetic Science Learning Center, University of Utah, http://learn.genetics.utah.edu.
Summary
-
How do I choose the appropriate techniques, instruments, and formulae to describe the dimensions of an object?
-
How can you measure the dimensions of objects of irregular shape or size?
In this lesson you examined various measuring instruments. You learned that a vernier caliper can measure the dimensions of small objects, such as the diameter of a dime. You learned that a trundle wheel can be used to measure the dimensions of large objects, such as the distance around a room. In order to accurately describe the dimensions of an object, you need to choose an appropriate measuring instrument and also the proper units. Knowing if an object is long or short, if the measurement should be in SI or imperial units, and also what instruments you have available will help you to choose an appropriate tool for measuring an object.
In this lesson you also found ways to measure the dimensions of irregular shapes. One way is to first use a piece of string to completely trace around the shape. Then stretch the string into a straight line and measure with a ruler. Another way is to input a related value, such as the diameter of a circle, into a mathematical formula.
In Lesson 3 you will learn how to convert measurements to different units within the same measurement system. You will also learn how to convert measurements between the SI system and the imperial system.




 inch or cm or m.
inch or cm or m.