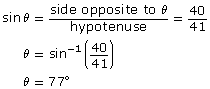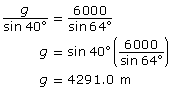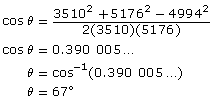Module 1 Summary
| Site: | MoodleHUB.ca 🍁 |
| Course: | Math 20-2 SS |
| Book: | Module 1 Summary |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 30 December 2025, 7:52 AM |
Description
Created by IMSreader
1. Module 1 Summary

David Hiller/Photodisc/Thinkstock
In this module you learned how to use trigonometry to determine distances and angles indirectly in situations involving right triangles as well as situations involving oblique triangles. Indirect measurement is required in many situations, such as the following:
- triangulation (the process used to create detailed maps over large distances)
- determining heights (for example, of buildings or cliffs)
In particular, you learned the following mathematics:
|
Math Idea |
Example |
|
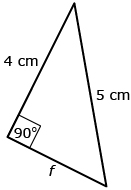
The Pythagorean theorem (a2 + b2 = c2) is only valid for right triangles. |
f2 + 42 = 52
f2 + 16 = 25
f2 = 9
f = 3 cm |
|
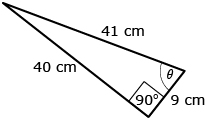
The primary trigonometric ratios (SOH CAH TOA) are only valid for right triangles.
|
|
|
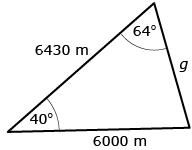
The sine law The sine law can also be described in words: “The length of a side divided by the sine of the opposite angle is the same for all side-angle pairs in any triangle.” |
|
|
The cosine law is valid for any triangle. There are two ways to write the cosine law, depending on whether you are solving for a missing side or a missing angle:
|
|