Heredity - Genetics
| Site: | MoodleHUB.ca 🍁 |
| Course: | Personal Psychology 20-RVS |
| Book: | Heredity - Genetics |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 26 December 2025, 9:31 AM |
1. DNA, Chromosomes and Genes
What is it that tells our bodies to do the things they do? How does a cell know to become a liver cell or a blood cell? Why are you taller than your brother? This is an introduction to the world of genes, an overview of the world of genetics in 30 seconds. Remember the study of genetics is a complex and changing topic.
2. Genes - how do they work?
Now that you have been introduced to the building blocks of a human, you will need to become familiar with a few important terms used by geneticists and with how traits, characteristics and diseases show up in a person.
This section will discuss genes, and their role in heredity. Learn the difference between alleles ( different expressions of a trait) and genes.
Watch this to learn the difference between phenoypes and genotypes. Phenotypes are the visible expression of a gene
(blue eyes) and genotypes are the actual combination of genetic information (alleles).
3. How are Characteristics passed on
What makes you who you are? How did you get your physical characteristics? The short answer is, it comes from you genetic makeup, which is passed to you from the combination of your parents' genes. In reality, we do not really know exactly how your genetic makeup and your environment effects your personality. This section will look at both the genetic and environmental influences that appear to effect your physical and psychological makeup.
This tutorial is a good overview of heredity and traits.
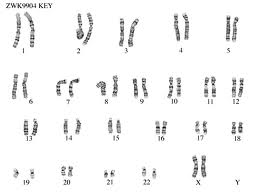
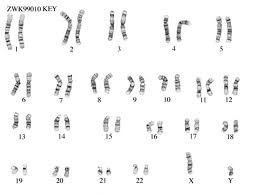
4. The Human Genome - Karyotypes
How do we know about our DNA?
Scientists can isolate an individual's chromosomes, stain them with dye and lay them out in what is called a Karyotype.
 |
 |
|
|
Normal Female karyotype showing 2 X's and 46 chromosomes total |
Normal Male karyotype showing X and Y and 46 chromosomes total |