Lesson 4
| Site: | MoodleHUB.ca 🍁 |
| Course: | Social 30-2 RVS |
| Book: | Lesson 4 |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Wednesday, 31 December 2025, 9:14 PM |
1. Introduction
Themes of Ideology
Issue Question: Should ideology be the foundation of identity?
_________
Key Issue: On which beliefs and values should my ideology be based?
Duration: 1 block (80 mins + homework)
Themes and Characteristics of Ideologies
Ideologies consist of various ideas or themes. Many ideologies have certain themes in common. Through these themes, people craft their beliefs and ideologies. Those things that people believe strongly help them to accept or reject ideologies and to act upon these beliefs accordingly.
Various societies, therefore, have developed their own ways of looking at the world. These societies can be influenced by how they interpret human nature. These societies must determine the answers to questions such as the following:
- Do some people deserve special privileges?
- What is our relationship to the land and the environment?
- What is the basis of our moral beliefs?
2
2. Lesson
Themes of Ideologies
Examine the information below to learn about the themes that are the foundations on which people base their beliefs. The themes of an ideology are those things about which people who believe in the ideology care deeply.
Nation
Some ideologies reflect beliefs and values related to the idea of nation. A nation may refer to a recognized country (such as Canada) or a group that sees itself as a nation: a group with common culture, history, heroes, language, customs
and goals.
A nation is concerned with sovereignty (independence), self-preservation, its own identity, citizenship, citizen participation, and the rights of its citizens. Sometimes a nation may hold extreme
views of its own rights in the world or its perceived needs, and these views may conflict with the views of others.

Religion
Religion is a key theme of some ideologies. Many religious beliefs and values pertain to ethics and morality. Religious observance may or may not play a major role in peoples' lives; however, the basic beliefs of religion are important to many currents of thought because religious beliefs answer questions about human nature, the way the world is, and the way the world should be.

Class
Class in society is a common theme of some ideologies. Social class refers to the way society is structured. In our society, class is usually based on occupations or the amount of money people have. Often people refer to the working class, the middle class, etc.
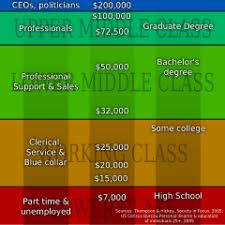
Relationship to Land and Environment
The relationship between humans and the land, or our environment, is another common theme in ideology. This theme is expressed both philosophically and practically (that is, in how we live in, interact with, and develop our environment).

Characteristics of Ideologies
Examine the information below to learn about the characteristics that are the basis of the worldviews of ideologies.
Interpretations of History
History is the story of how we got to be who we are and of what society was like in the past. Just as two people viewing the same accident will tell police two different accounts of the accident, people interpret the past differently based on their core beliefs and values. People who share an ideology, however, are unlikely to interpret the past in a similar way.
A nation interprets its history, and their interpretation then becomes part of the nation's ideology.
All people or groups act based on their ideologies and every ideology attempts to answer the questions "What are humans like?" and "What should society be like?"
Any exploration of what humans are like involves exploring what makes humans human. What do you think? Can you think of biological, sociological, and emotional qualities that make humans human?
Influential Philosophers
Over the centuries, many people have thought about, talked about, and written about human nature, and, in so doing, they have contributed to the development of ideologies. In this course you will focus on five of the following philosophers, who have had a profound impact on shaping Western economic and political ideologies: Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Karl Marx and Adam Smith.

Interpretations of history are often demonstrated in acts of patriotism. How do certain celebrations reflect a specific interpretation of history?

What makes humans human?

Karl Marx
Beliefs About Society
A question that all ideologies address is "What is the nature of society?" Some societies are built on the principles of peace and goodwill, while others are built on tyranny and fear. Ideologies are the foundations on which all societies are structured, for good or bad, because ideologies are ways of understanding how we should interact with one another.

How should we interact with each other?
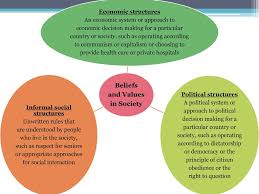
Beliefs about the Structure of Society
As shown in the diagram to the right, society can be seen as having three main parts: informal social structures, economic structures, and political structures. What these structures are like depend on the beliefs and values of the people who live in the society and their worldview, which can change over time.
Informal Social Structures of Society
Informal social structures of society are the unwritten rules about acceptable social behaviour and actions. Informal social structures also include the relationships that form between people and how people interact with one another.
Economic Structures of Society
The salaries that people earn, what work they do, and who benefits from their work can tell a great deal about the beliefs and values of a society. Differences in the beliefs and values regarding economic structures of society have resulted in the opposing ideologies of capitalism and communism.Political Structures of Society
All societies are organized so that the people who live in and are governed by them know how to behave "properly." Different societies define "proper" behaviour differently. In a democracy, a good citizen can disagree with and challenge the government. In a non-democratic society, a good citizen is one who agrees with and obeys the government.
Beliefs and Values in Society
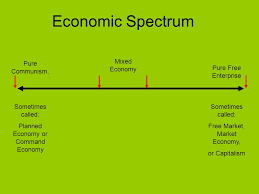
Economic Spectrum
When you place the two ideologies on an economic spectrum, they would be at opposite ends: communism on the left with collectivism, and capitalism on the other end with individualism
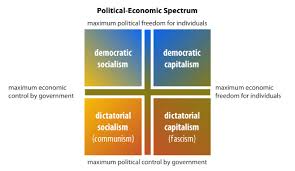 Differences in the beliefs and values regarding the economic structures of society have resulted in the ideologies of capitalism and socialism, among others.
Differences in the beliefs and values regarding the economic structures of society have resulted in the ideologies of capitalism and socialism, among others.
Visions of the Future
Most ideologies include a vision of what the world should be like in the future, based on the beliefs and values of the ideology in question. For example, Karl Marx, a founder of communist ideology, had a vision of the future in which people would be completely free to explore any pursuit they wished.
Want More Information?
Please refer to pages 28 to 38 in your textbook.
What is your vision of the future?

Understandings of Ideologies
3. Assignment

Assignment One of One (10 marks)
Read The Caste System on page 40 in your textbook, Understandings of Ideologies. Then, discuss the following question.
- In exploring the caste system in India, what insights have you gained about your own beliefs and values? With which side of the issue (whether society should be divided along class lines or not) do you agree with more? Why?
Post your answer to this question in the U1L4 Caste Discussion
You will be evaluated based on this rubric.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the themes of ideology serve as the basis for how a group of like-minded people respond to issues and determine what is important to them. These themes inform decision-making concerning issues that affect their way of life.