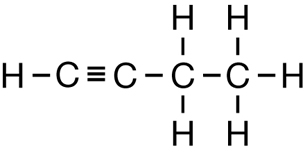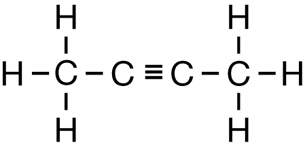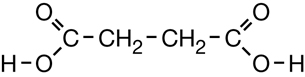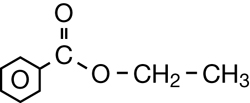Unit C Conclusion
 Unit C Diagnostic Self-Check
Unit C Diagnostic Self-Check
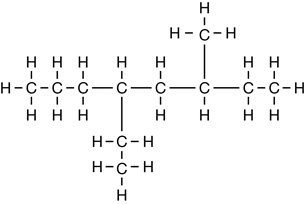
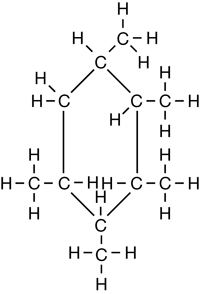
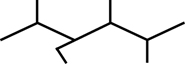
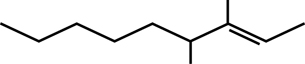
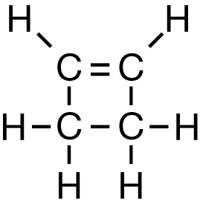
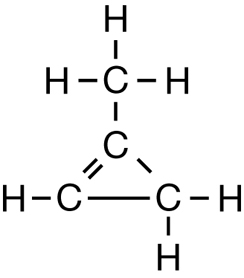
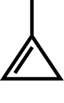
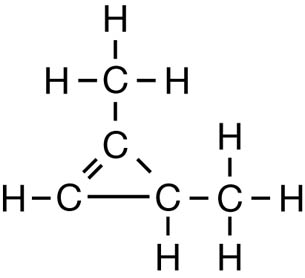
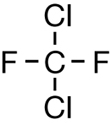
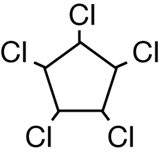
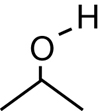
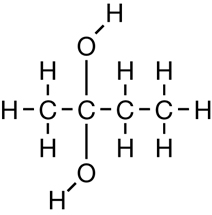
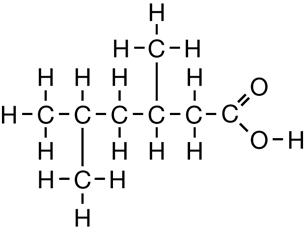
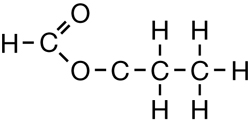
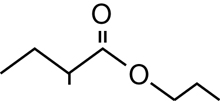
SC 1. Consider the following diagrams:
- State the systematic name for each of the four compounds shown.
- Identify which of the molecules shown are isomers.
Program of Studies
SC 1.
30-C1.3k. Students will
- name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) and aromatic carbon compounds
30-C1.5k. Students will
- define structural isomerism as compounds having the same empirical formulas, but with different structural formulas, and relate the structures to variations in the properties of the isomers
30-C1.3s. Students will
- follow appropriate IUPAC guidelines when writing the names and formulas of organic compounds
Hint
SC 1. The systematic naming system uses prefixes and suffixes to describe aspects of the chemical structure of organic compounds.
Isomers are molecules that have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 1.
Molecule |
Systematic Name |
Chemical Formula |
Corresponding Isomer |
A |
4-ethyl-6-methyloctane |
C11H24 |
C |
B |
1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclohexane |
C11H22 |
D |
C |
3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethylhexane |
C11H24 |
A |
D |
3,4-dimethylnon-2-ene |
C11H22 |
B |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 1. Module 5 Lessons 2–4
Use the following information to answer SC 2–SC 4.
A technologist is studying the following molecules that have between seven and eight carbons each.
- hexane
- 2-methylhexane
- pentane
- 2-methylpentane
- 2,2-dimethylbutane
SC 2. Draw the chemical structures, condensed structural diagrams, and line diagrams for the molecules listed.
Program of Studies
SC 2.
30-C1.3k. Students will
- name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) and aromatic carbon compounds
30-C1.3s. Students will
- follow appropriate IUPAC guidelines when writing the names and formulas of organic compounds
Hint
SC 2. The systematic naming system using prefixes and suffixes to describe aspects of the chemical structure of organic compounds.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 2.
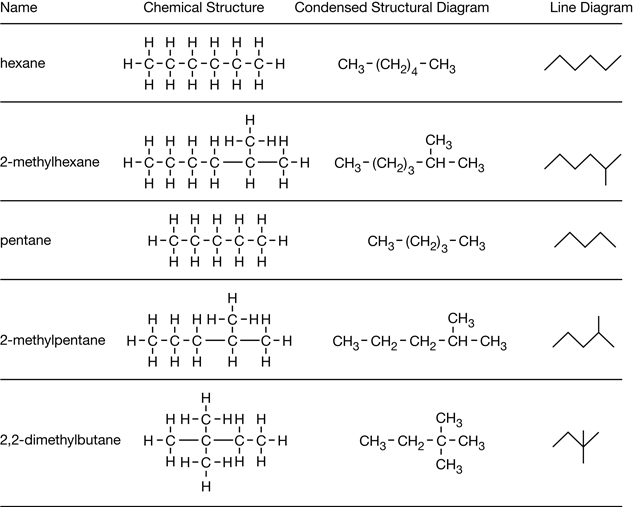
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 2. Module 5 Lesson 2
SC 3. Rank the molecules listed in order of increasing boiling point.
Program of Studies
SC 3.
30-C1.6k. Students will
- compare, both within a homologous series and among compounds with different functional groups, the boiling points and solubility of examples of aliphatics, aromatics, alcohols and carboxylic acids
Hint
SC 3. Recall that boiling points for hydrocarbons are influenced by intermolecular forces (namely London forces) and by their shape.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 3.
Ranking (from lowest to highest boiling temperature) |
Rationale |
Actual Boiling Point (°C) |
pentane |
smallest molecule, smallest strength of London forces |
36.1 |
2,2-dimethylbutane |
six-carbon molecule, but branching decreasing ability to closely associate with neighbouring molecules, thereby decreasing strength of London forces |
49.7 |
2-methylpentane |
six-carbon molecule, but branching decreasing ability to closely associate with neighbouring molecules, thereby decreasing strength of London forces only one branch, therefore reduction in attractive forces not as severe as 2,2-dimethylbutane |
60 |
hexane |
six-carbon molecule, no branching increases ability to closely associate with neighbouring molecules, thereby increasing strength of London forces |
69 |
2-methylhexane |
largest molecule (seven carbons), largest strength of London forces |
90 |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 3. Module 5 Lesson 5
SC 4. If the five hydrocarbons listed made up a mixture, describe an experiment that could be used to separate the five compounds. Include a description of the equipment you would use and safety information related to the equipment.
Program of Studies
SC 4.
30-C1.1.s. Students will
- design a procedure to separate a mixture of organic compounds, based on boiling point differences
30-C1.7k. Students will
- describe, in general terms, the physical, chemical and technological processes (fractional distillation and solvent extraction) used to separate organic compounds from natural mixtures or solutions; e.g., petroleum refining, bitumen recovery
Hint
SC 4. Recall the kinds of equipment and processes used to separate the various components of petroleum.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 4. A fractional distillation experiment could be set up whereby the mixture is heated and the components evaporate at their boiling temperatures. Each component can be collected and stored.
Safety concerns include the flammability of the components; therefore, no flames should be involved.
Necessary equipment includes a distillation apparatus that connects to the flask that will contain the mixture. The contents of the flask can be heated using an electric mantle or a water bath heated using a hot plate.
Organic compounds of this molecular mass tend to vapourize easily. To reduce exposure to the fumes, the entire experiment should be conducted within a fume hood.
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 4. Module 5 Lesson 5
SC 5. Write condensed and line structural diagrams for the molecules with the chemical formula C4H6.
Program of Studies
SC 5.
30-C1.3k. Students will
- name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsaturated aliphatic (including cyclic) and aromatic carbon compounds
30-C1.5k. Students will
- define structural isomerism as compounds having the same empirical formulas, but with different structural formulas, and relate the structures to variations in the properties of the isomers
Hint
SC 5. The carbon atoms in an organic molecule can form a continuous chain, cyclic arrangement, or have branches of shorter alkyl chains.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 5.
Isomers of C4H6
Condensed Structural Diagram |
Line Structural Diagram |
Name |
|
|
butyne |
|
|
but-2-yne |
|
|
cyclobutene |
|
|
methylcyclopropene |
|
|
2- methylcyclopropene |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 5. Module 5 Lessons 2 and 3
Use the following information to answer SC 6 and SC 7.
A student tested two liquid samples containing a pure hydrocarbon.
Sample |
Test |
Result |
A |
addition of aqueous bromine |
The resulting mixture was colourless. |
B |
The resulting mixture was brown. |
SC 6. Describe the purpose of this test and what properties of hydrocarbons the test identifies.
Program of Studies
SC 6.
30-C1.3s. Students will
- interpret the results of a test to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated aliphatic, using aqueous bromine or potassium permanganate solutions
Hint
SC 6. What does the term saturated mean when referring to a hydrocarbon?
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 6.
The purpose of this test is to detect the extent of saturation of a hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons will not react spontaneously with bromine, whereas unsaturated hydrocarbons will. Unsaturated hydrocarbons possess multiple bonds that are readily broken as bromine atoms, and the hydrocarbon undergoes an addition reaction.
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 6. Module 6 Lesson 2
SC 7. Group the following molecules into one of the samples shown in the table above (i.e., Sample A or Sample B):
- hexane
- hexene
- cyclohexane
- cyclohexene
- benzene
Program of Studies
SC 7.
30-C1.3s. Students will
- interpret the results of a test to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated aliphatic, using aqueous bromine or potassium permanganate solutions
Hint
SC 7. What chemical structures are responsible for unsaturations?
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 7.
Sample |
Substance |
A |
hexene |
B |
hexane |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 7. Module 3 Lesson 2
SC 8. Complete the following table:
Name |
Functional Group |
Aspects or Properties |
Uses |
Methane |
|
|
|
Methanol |
|
|
|
Ethane |
|
|
|
Ethanol |
|
|
|
Ethanoic Acid |
|
|
|
Propane |
|
|
|
Benzene |
|
|
|
Octane |
|
|
|
Glucose |
|
|
|
Polyethylene |
|
|
|
Program of Studies
SC 8.
30-C1.2k. Students will
- identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life, demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications; e.g., methane, methanol, ethane, ethanol, ethanoic acid, propane, benzene, octane, glucose, polyethylene
Hint
SC 8. How does the name of an organic compound indicate important parts of its chemical structure? What are some common uses of organic compounds?
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 8.
Name |
Functional Group |
Aspects or Properties |
Uses |
Methane |
none—hydrocarbon |
saturated, gas, insoluble in water |
fuel (heating ) |
Methanol |
hydroxyl (alcohol) |
soluble in water |
fuel |
Ethane |
none—hydrocarbon |
saturated, gas, insoluble in water |
feedstock for making ethene and other petrochemicals |
Ethanol |
hydroxyl (alcohol) |
soluble in water |
alcoholic beverages, fuel |
Ethanoic Acid |
carboxyl (carboxylic acid) |
soluble in water |
vinegar |
Propane |
none—hydrocarbon |
saturated, gas, insoluble in water |
feedstock for making other petrochemicals |
Benzene |
benzene ring |
behaves like a saturated hydrocarbon, insoluble in water |
petrochemical |
Octane |
none—hydrocarbon |
saturated, liquid, insoluble in water |
feedstock for making other petrochemicals and automobile fuels |
Glucose |
hydroxyl (multiple groups) |
carbohydrate (sugar) |
energy source for cells |
Polyethylene |
polymer |
large molecule |
plastic for consumer goods |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 8. Modules 5 and 6
SC 9. Complete the following table:
Structural Diagram |
Functional Group |
Class |
Systematic Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program of Studies
SC 9.
30-C1.4k. Students will
- identify types of compounds from the hydroxyl, carboxyl, ester linkage and halogen functional groups, given the structural formula
Hint
SC 9. Can you identify the functional group on each of the molecules in the table? How does the presence of a functional group influence the systematic name for an organic compound?
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 9.
Structural Diagram |
Functional Group |
Class |
Systematic Name |
|
halogen |
organic halide |
dichlorodifluoromethane |
|
halogen |
organic halide |
1,2,3,4,5-pentachlorocyclopentane |
|
hydroxyl |
alcohol |
propan-2-ol |
|
carboxyl |
carboxylic acid |
butane-1,4-dioic acid |
|
hydroxyl |
alcohol |
butane-2,2-diol |
|
carboxyl |
carboxylic acid |
pentanoic acid |
|
carboxyl |
carboxylic acid |
3,5-dimethylhexanoic acid |
|
ester |
ester |
ethyl methanoate |
|
ester |
ester |
propyl-2-methyl butanoate |
|
ester |
ester |
ethyl benzoate |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 9. Module 6
Use the following chemical reactions to answer SC 10 and SC 11.
-
elimination reaction with butane as a reactant
-
elimination reaction with butan-2-ol as a reactant
-
elimination reaction involving 2-iodobutane and hydroxide ion as reactants
-
addition reaction between fluorine and cyclopentene
-
addition reaction between 2-pentene and water
-
substitution reaction between chlorine and benzene
-
combustion reaction for propane
-
combustion reaction for propan-2-ol
-
esterification reaction between ethanol and 2-methylpropanoic acid
-
esterification reaction between butan-2-ol and methanoic acid
SC 10. Using materials in you home, construct molecular models of the reactants and the products in the chemical reactions shown:
Program of Studies
SC 10.
30-C2.1k. Students will
- define, illustrate and provide examples of simple addition, substitution, elimination, esterification and combustion reactions
30-C2.2k. Students will
- predict products and write and interpret balanced equations for the above reactions
Hint
SC 10. How does knowing the type of reaction provide a clue to the products that will result?
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 10. Module 6 Lessons 2–6
SC 11.Write the balanced chemical reaction for each of the chemical reactions provided, and write the name for each chemical substance involved in the reactions.
Program of Studies
SC 11.
30-C2.1k. Students will
- define, illustrate and provide examples of simple addition, substitution, elimination, esterification, and combustion reactions
30-C2.2k. Students will
- predict products and write and interpret balanced equations for the above reactions
Hint
SC 11. What is the most common molar ratio, or proportion for reactants, in organic reactions?
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 11.
The reactions are shown using chemical formulae; other representations could be used.
Reaction |
Reactants |
|
Products |
||||
A |
C4H10 |
→ |
C4H8 |
+ |
H2 |
||
|
butane |
|
butene (or but-2-ene) |
|
hydrogen |
||
B |
C4H8OH (or C4H9O) |
→ |
C4H8 |
+ |
H2O |
||
|
butan-2-ol |
|
but-2-ene |
|
water |
||
C |
C4H9I |
+ |
OH- |
→ |
C4H8 |
+ |
H2O + I- |
|
iodobutane |
|
hydroxide ion |
|
butene |
|
water and iodide ion |
D |
C5H8 |
+ |
F2 |
→ |
C5H8 F2 |
||
|
cyclopentene |
|
fluorine |
|
1,2-difluorocyclopentane |
||
E |
C5H10 |
+ |
H2O |
→ |
C5H11OH (or C5H12O) |
||
|
pent-2-ene |
|
water |
|
pentan-2-ol |
||
F |
C6H6 |
+ |
Cl2 |
→ |
C6H5Cl |
+ |
H-Cl |
|
benzene |
|
chlorine |
|
chlorobenzene |
|
hydrogen chloride |
G |
C3H8 |
+ |
5 O2 |
→ |
3 CO2 |
+ |
4 H2O |
|
propane |
|
oxygen |
|
carbon dioxide |
|
water |
H |
C3H7OH (or C3H8O) |
+ |
4.5 O2 |
→ |
3 CO2 |
+ |
4 H2O |
|
propan-2-ol |
|
oxygen |
|
carbon dioxide |
|
water |
I |
C3H7COOH (or C4H8O2) |
+ |
C2H5OH (or C2H6O) |
→ |
C3H7COOC2H5 (or C6H12O2) |
+ |
H2O |
|
2-methylpropanoic acid |
|
ethanol |
|
ethyl-2-methyl propanoate |
|
water |
J |
C3H7COOH (or C4H8O2) |
+ |
CH3OH (or CH4O) |
→ |
C3H7COOCH3 (or C5H10O2) |
+ |
H2O |
|
2-butanoic acid |
|
methanol |
|
methyl butanoate |
|
water |
Lesson(s) to Review
SC 11. Module 6