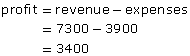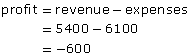Lesson 1
1. Lesson 1
1.2. Explore
Module 2: Number
Explore

Hemera/Thinkstock
What you may have discovered in Share 1 is that regardless of the business, there are commonalities in expenses. To cover the cost of expenses, businesses sell products or services to earn revenue.
|
Expenses |
Revenue |
Definition |
money required for the business to operate |
total money earned by the business |
Common Examples |
|
|
In general, businesses earn sales revenue by selling goods or services. In the course of delivering those goods or services, businesses have associated expenses. If their revenue is higher than their expenses, they make a profit; if their revenue is lower than their expenses, they incur a loss. If their revenue is equal to their expenses, they break even.
|
|
|
revenue – expenses = negative |
revenue – expenses = positive |
revenue – expenses = 0 |
In Share 1 you had a variety of expenses. These can be categorized as either fixed or variable. Fixed expenses are the same amount and occur at a regular frequency, such as the cost to rent a building per month. Variable expenses are varying amounts that may or may not occur at a regular frequency, such as fuel and repair costs for a vehicle. You may also have fixed and variable revenue. Fixed revenue could come from a long-term contract where you expect the same amount of money each month over an extended period. Variable revenue could come from a one-time contract that you do not expect to be repeated.
In the table, examples are given for these definitions as applied to a small landscaping business.
Revenue |
The landscaping business will earn money by providing landscaping services to customers. |
Expenses |
The company will have many different expenses, including
|
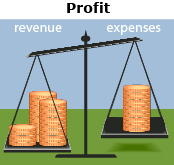
Profit (positive profit) |
Suppose the business had revenue of $7300 and expenses of $3900 in a month.
The profit is positive, so the company had a profit of $3400 that month. |
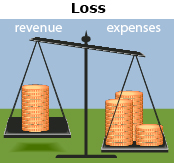
Loss |
Suppose the business had revenue of $5400 and expenses of $6100 in a month.
The profit is negative, so the company lost $600 that month. |
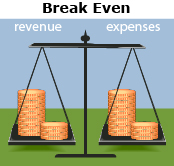
Break Even (zero profit) |
Suppose the business had revenue of $6300 and expenses of $6300 in a month.
The profit is zero, so the company broke even that month. |
Fixed Expenses |
Some fixed expenses for the landscaping company include
|
Variable Expenses |
Some variable expenses for the landscaping company include
|
Fixed Revenue |
The company has contracts with some customers to cut their lawn every week. |
Variable Revenue |
The company has some customers who ask for one-time services. |

BananaStock/Thinkstock
The way money is moving into and out of a business can be summarized by a statement of revenue and expense. A sample statement of revenue and expense for a landscaping business is shown in the following table. Notice that all the revenues are totalled and all the expenses are totalled in the statement. These totals are then used to determine the profit.
 |
|||
September 2013 |
|||
Income ($) |
Expenses ($) |
||
Regular Contracts One-time Contracts |
8150 1200 |
Wages Fuel Repairs Insurance Supplies Rent |
3200 365 190 110 680 1400 |
Total |
9350 |
|
5945 |
PROFIT |
|
||