Lesson 4
1. Lesson 4
1.6. Explore 2
Module 5: Geometry
In Try This 2, you may have noticed that a coordinate grid can be useful when describing a translation. In fact, a coordinate grid will prove useful for all of the transformations discussed in this module.
Watch Translation Explanation to see how a formula can be used to describe what translations are applied to an object.
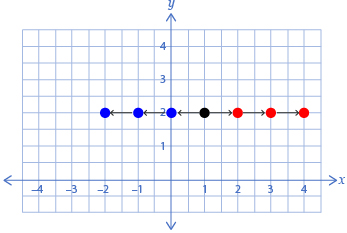
To move an object left or right, you can decrease or increase the x-values of the point’s coordinates. For example, suppose the point (1, 2) is a vertex of an object. To move the vertex left or right, you change the x-value, which, in this case, is 1.
Movement from (1 , 2) |
Change in Coordinates |
New Coordinates |
left 3 |
(1 − 3, 2) |
(−2, 2) |
left 2 |
(1 − 2, 2) |
(−1, 2) |
left 1 |
(1 − 1, 2) |
(0, 2) |
not moved |
(1, 2) |
(1, 2) |
right 1 |
(1 + 1, 2) |
(2, 2) |
right 2 |
(1 + 2, 2) |
(3, 2) |
right 3 |
(1 + 3, 2) |
(4, 2) |
Similarly, to move an object up or down you can increase or decrease the y-value of its coordinates.
Self-Check 1
![]()