Lesson 2: Ionic and Molecular Compounds
2. Intramolecular Bonding in Ionic Compounds
Electronegativity(EN) is a value that describes the relative attraction of an element to electrons. When two elements form a bond, the electronegativity values for each will indicate how ionic or covalent the bond will be. The larger the difference in EN, the more the intramolecular bond will be.
Valence electrons (ve) are electrons in the highest or outermost, the energy level of the atom. These electrons are the ones that involve in a chemical reaction.
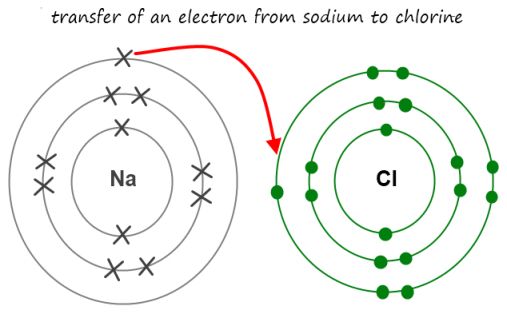
Ionic bonding is found between metals and nonmetals. In general, metals have low EN whereas non-metals have high EN values. When forming an ionic bond, metals lose one or more of their valence electrons. The resulting positively charged cation will have the same electron configuration as the nearest noble gas has.
Example:
Na-e- --> Na+ has the same number of ve as Ne (10).
Cl+e- --> Cl_ has gained one electron to have the same ve as Ar to become more stable. The ionic bond that for between a Na and Cl ions is due to an attraction between opposite charges.
The intramolecular forces within the crystal lattices of ionic solids are the electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions.
Ionic compounds consist of ions held together by strong ionic bonding forming a lattice structure. A significant amount of energy is needed to split the lattice. Therefore, ionic compounds have high melting points, are solid at room temperature.
Most ionic compounds dissociate in water due to water molecule's partially positive and negative ends. These opposite ends will be attracted to cations and anions to break the bond. This process will require energy to break bonds.
When the energy released, as the ionic bond breaks, is greater than the energy used to break apart an ionic solid into individual ions, the ionic solid will dissolve in water. Otherwise, it will be insoluble in water.
Ionic compounds react as individual ions. In crystalline form, ionic compounds don't react easily. In an aqueous state, the ionic compound exists as individual ions. Therefore, ionic compounds dissolved in water react more easily than solid ionic compounds.