Lesson 2: Ionic and Molecular Compounds
4. Naming Molecular Compounds
Binary molecular compounds are named using a system of prefixes which indicate the number of first atoms in the compound. The second atom in the formula gets an -ide ending. The prefix mono is used on the second atom only.
| Number | Prefix | Number | Prefix |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mono | 6 | hexa |
| 2 | di | 7 | hepta |
| 3 | tri | 8 | octa |
| 4 | tetra | 9 | nona |
| 5 | penta | 10 | deca |
As2O3: diarsenic trioxide
H2O: dihydrogen monoxide (water)
Non-binary molecular compounds, mostly organic, has a different system of nomenclature.
- Write out the symbol of the elements in the compound.
- The first element keeps its name, the second element ends with -ide.
Ex. NF3: Nitrogen trifluoride
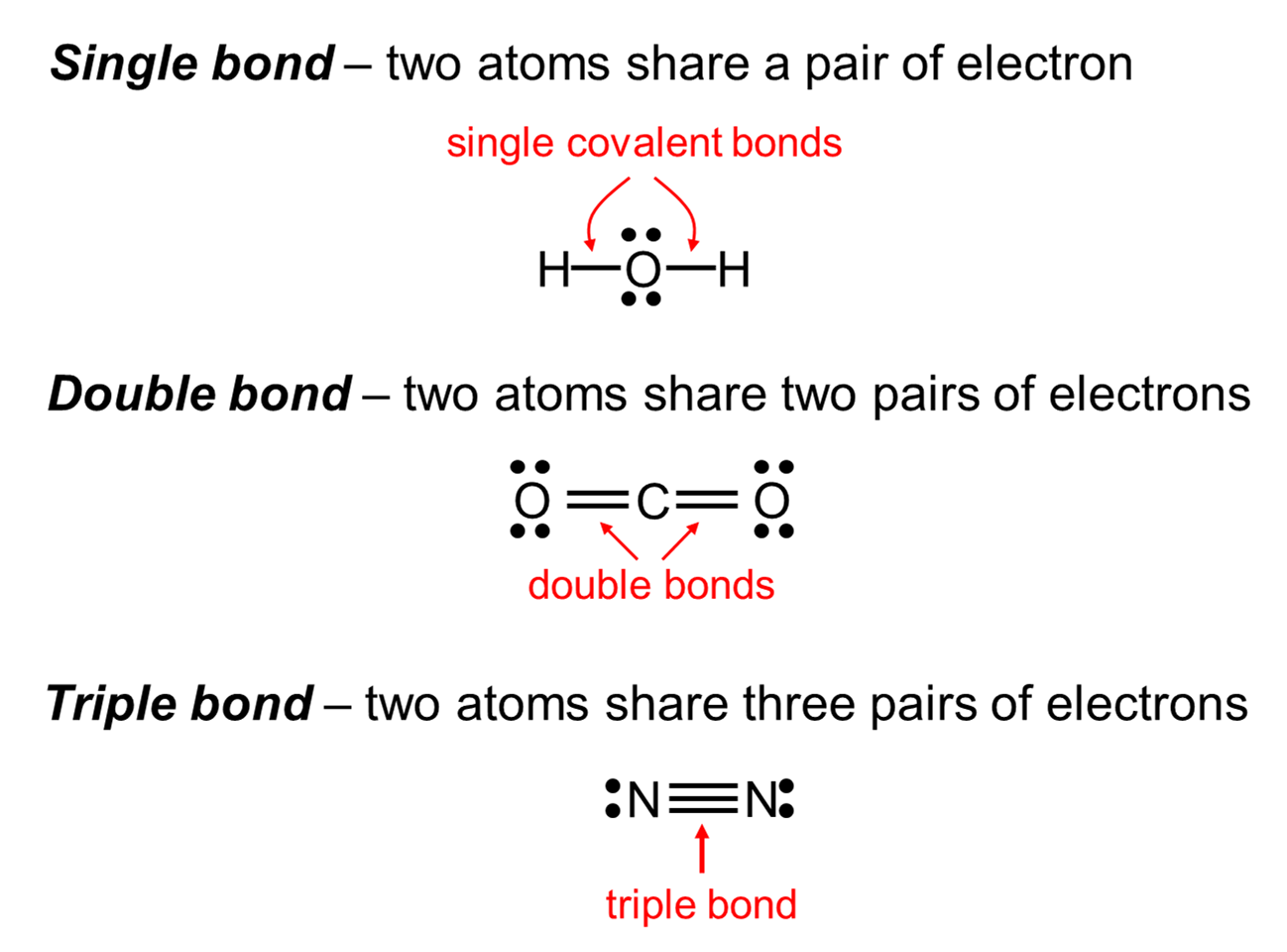
Molecular compounds are composed of non-metals. The atoms within molecules are held together by covalent bonds where atoms share electrons.
The chemical formula for a molecular compound represents the actual number of atoms that form the molecule. For instance, CO2 contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. A covalent on is the attraction of two nuclei for a pair or pairs electrons that they share.
If one pair of election is shared, a single covalent bond is formed. If two pairs of electrons are shared, then a double covalent bond is formed.