Lesson 1: Clinical Disorders – Part F
PART F
What Do Drugs Do to the Brain?
The brain is a very complex organ that we rely on for everything we do. It is made up of many parts that work together. Drugs can alter important brain areas that are necessary for life-sustaining functions and can drive the compulsive drug abuse that marks addiction. There are three areas of the brain that are affected by drug abuse. They include: the brain stem, cerebral cortex, and limbic system.
Let`s look at what each part controls...
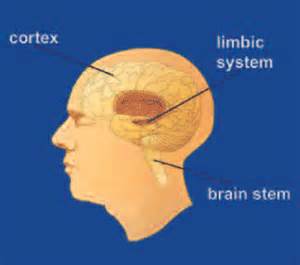 brain stem - controls the basic functions that are critical to life such as heart rate, breathing and sleeping.
brain stem - controls the basic functions that are critical to life such as heart rate, breathing and sleeping.
cerebral cortex - Different area of the cortex control specific functions that allow us to process information from our senses, enabling us to see, feel, hear and taste. The frontal part of the cortex is the thinking center of the brain and allows us to think, plan, solve problems and make decisions.
limbic system - It links together a number of brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure. Feeling pleasure motivates us to repeat behaviours that are essential to our existence. The limbic system is activated by healthy life-sustaining activities such as eating and socializing, but it is also activated by drugs of abuse. The limbic system is responsible for our perception of emotions, whether positive or negative, which explains the mood-altering properties of many drugs.
Some drugs lock onto the neuron and act like a pump, so the neuron releases more neurotransmitters. Other drugs block re-absorption or reuptake and cause unnatural floods of neurotransmitters. All drugs of abuse, such as nicotine, cocaine, and marijuana, primarily affect the brain’s limbic system. Scientists call this the “reward” system. Normally, the limbic system responds to pleasurable experiences by releasing the neurotransmitter dopamine, which creates feelings of pleasure.
Some drugs work in the brain because they have a similar size and shape as natural neurotransmitters. In the brain, in the right amount or dose, these drugs lock into receptors and start an unnatural chain-reaction of electrical charges causing neurons to release large amounts of their own neurotransmitter.
Since each drug has its own unique chemical structure, they work differently. However, we do know that there are at least two ways drugs work in the brain:
- Imitating the brain's natural chemical messengers
- Overstimulating the "reward circuit" of the brain (which occurs in the limbic system)
The following two web site provides a wealth of information about the different drugs and how they affect the brain.
|
http://teens.drugabuse.gov/drug-facts/brain-and-addiction http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugs-brains-behavior-science-addiction/drug-abuse-addiction |