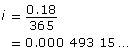Lesson 6
1. Lesson 6
1.5. Explore 4
Module 6: Exponents and Logarithms
In Try This 4 you will explore how exponential equations can be used to solve problems involving investments and credit cards.
Try This 4

Hemera/Thinkstock
Answer the following questions using the compound interest formula A = P(1 + i)n, where
- A is the future value
- P is the present value
- i is the interest rate per compounding period, as a decimal
- n is the number of compounding periods
Scenario 1
Eoghan (pronounced Ewan) receives a gift of $500 and decides to invest in a GIC (guaranteed investment certificate) that earns 5.5% per year, compounded semi-annually. Determine how long it will take for Eoghan’s GIC to be worth $700 by answering the following questions.
- Determine the following variables, and identify the unknown variable.

- A
- P
- i

- n
- Substitute the values from question 1 into the formula A = P(1 + i)n. Solve for the unknown variable.

- Use your answer from question 2 to determine how many years it will take for the GIC to be worth $700.

iStockphoto/Thinkstock
Scenario 2
Jia used a credit card to purchase an $850 tablet computer. The interest rate charged on overdue balances is 18% per year, compounded daily. Answer the following questions to determine how many days Jia’s payment is overdue if the amount owed on her credit card is $875.
- Use the compound interest formula to determine the following variables. Make sure to identify the unknown variable.

- A
- P
- i

- n
-
Substitute the values from question 4 into the formula A = P(1 + i)n. Solve for the number of days the balance is overdue.

- Compare the procedures you used to solve questions 2 and 5. What stayed the same and what changed in the two procedures?
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.

Comstock/Thinkstock
The Diners Club, introduced in 1950, was the first universal credit card. Today, many adults have at least one credit card. In fact, to rent a car, you must have a credit card. There is an element of risk to a financial institution in extending credit to individuals. Many credit cards charge a high interest rate on balances not paid after a month. These interest rates are usually compounded daily.