Lesson Two: The Origins of Western Democratic Liberalism
7. Lesson 3.2.6 John Stuart Mill

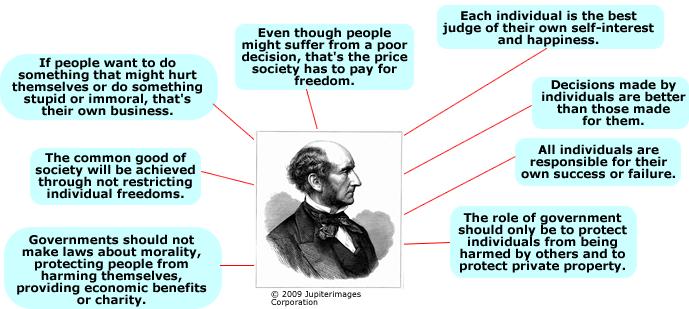
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (1806-1873) and Classical Political Liberalism
John Stuart Mill was a political thinker who believed that most people are logical and rational and will behave appropriately. He believed that there was no need for strict government control. Mill felt that society did not need restrictions. He questioned the need for laws that would restrict individual freedom to choose. Mill believed that the common good would benefit from placing the least amount of restrictions possible on individual rights and freedoms.
Mill argued that legal and political freedoms would create a society that would provide more liberty for all. He believed that government should
have a limited role in restricting the rights and freedoms of individuals
maintain and protect the rule of law
protect private property
protect the rights and security of the individual
Some basic principles of classic political liberalism according to John Stuart Mill are the following:
To reinforce the ideas you just learned about please read pages 101-110 in your textbook, Understandings of Ideologies. Answer the following questions as you complete your reading.
The Origins of Western Democratic Liberalism (p. 101-110)
1. Examine the diagram on page 103. How was society structured in Europe between the 1700’s and 1800’s?
2. What revolution was taking place during this time? Give a minimum of three examples of how it changed peoples’ lives. (p. 102, paragraph 3)
3. Read the caption attached to figure 4-6. Why did liberalism begin to develop in Europe during this period?
4. Whose writing challenged the traditional economic ways of thinking? What were his main criticisms of mercantilism? (p. 103, paragraphs 3, 4)
5. Explain how he thought competition and self interest would create a strong economy? (p. 104, paragraph 1)
6 Explain the “invisible hand.” (p. 104 paragraph 1)
7. Examine figure 4-8 and read the text with it. Explain the law of “supply and demand.”
8. What are the advantages of capitalism over mercantilism? (another thinking question)
9. How do Smith’s ideas reflect the values of classic liberalism. (yup, another thinking one)
10. What are the key political elements of liberal democracy?
(p. 106, paragraph 1)
11. What ideas did John Stuart Mill contribute to the ideas of liberalism?
(p. 107, paragraph 2)
12. Examine the “Voices Box” on page 108 and answer questions 1-3.
13. How does classical liberalism differ from modern liberalism?
(your last thinking question of the worksheet)
Self check your answers here.