Lesson 1
1. Lesson 1
1.12. Lesson 1 Summary
Module 5: Trigonometry Applications and Identities
Lesson 1 Summary
In this lesson you explored the tangent function. The tangent function can be defined as the y-coordinate of the intersection of the terminal arm and a vertical line tangent to the right side of the unit circle as shown in the diagram.
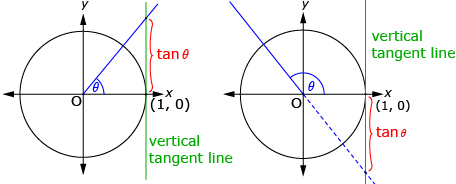
When the terminal arm is in quadrant 1 or quadrant 4, the intersection of the terminal
arm is used. When the terminal arm is in quadrant 2 or quadrant 3, an extension of
the terminal arm is used.
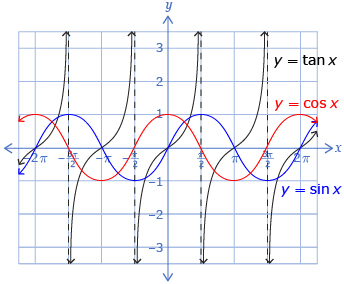
Although y = tan x is periodic, it is very different from y = sin x or y = cos x. The function y = tan x is not defined for all x values, and its graph contains vertical asymptotes and has no minimum or maximum value.
sin θ, cos θ, and tan θ are related by the equation ![]() and the slope of the terminal arm in standard position at angle θ is equal to tan θ.
and the slope of the terminal arm in standard position at angle θ is equal to tan θ.
In Lesson 2 you will examine how a problem can be solved using a trigonometric model.