Lesson 1
1. Lesson 1
1.2. Explore
Module 3: Permutations, Combinations, and the Fundamental Counting Principle
Explore
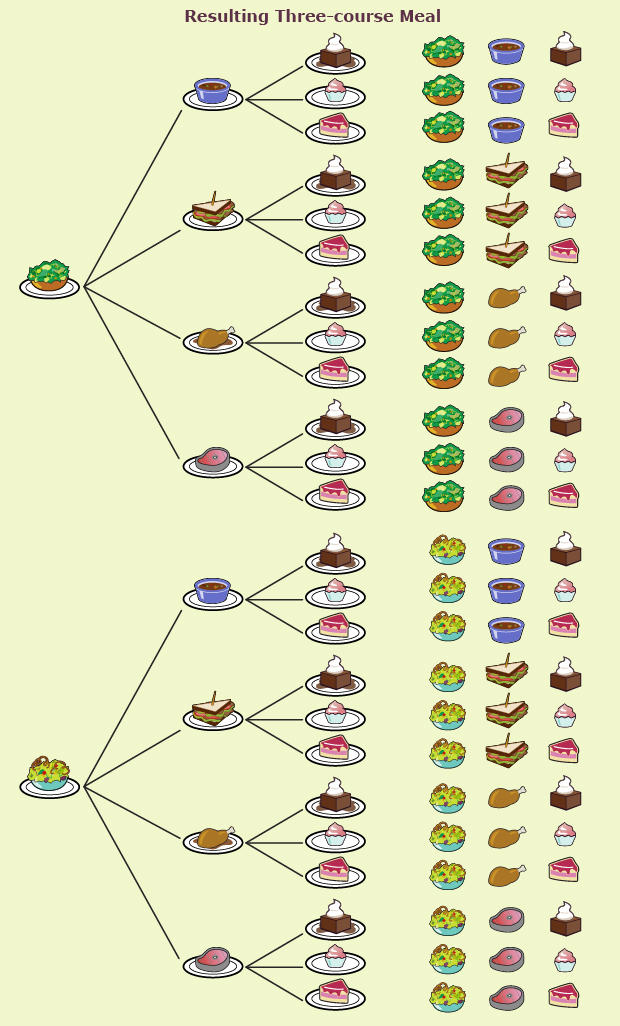
In Share 1, someone may have suggested using a diagram to solve the problem. The following diagram is called a tree diagram.
Adapted from © gollli/26357551/Fotolia
By counting the total number of terminal branches in the tree diagram, you can see that you have a choice of 24 three-course meals. The list of all 24 possible meals is called the sample space for this problem. Remember from Module 2 that the sample space is a list of all possible outcomes. You could also list all possible outcomes in an outcome table. A partial table is shown.
Salad |
Entrée |
Dessert |
mixed |
chili |
brownie |
mixed |
chili |
cupcake |
mixed |
chili |
cheesecake |
mixed |
club sandwich |
brownie |
mixed |
club sandwich |
cupcake |
mixed |
club sandwich |
cheesecake |

Hemera/Thinkstock
The first example on Tree Diagram at Mathematics Glossary demonstrates how all possible outcomes of tossing a penny and rolling a die can be calculated using a tree diagram. Note that the order of tossing the penny or rolling the die does not affect the outcomes or sample space.
In the next Try This, you will find the possible outcomes using tree diagrams and outcome tables. You will then determine an expression to calculate these outcomes.
Try This 2
Complete “Investigate the Math” questions A, B, C, D, E, F, and G on pages 66 and 67 of your textbook. ![]()
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.