Module 5 Intro
1. Module 5 Intro
1.25. Page 2
Module 5—Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Explore
Explore
 Read
Read
Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen is not present. When oxygen isn’t present, common anaerobic respiration by-products are sulfur, nitrite, methane, and odourless carbon dioxide. The colon contains bacteria that function without oxygen. By-products of this respiration in people are smelly gases. You will explore anaerobic respiration further as you move through this lesson.
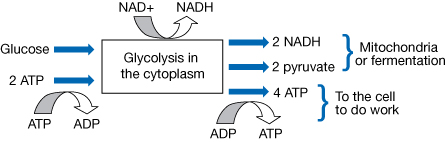
Consider the following diagram.

glycolysis: a metabolic pathway in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two, 3-carbon molecules and a small amount of ATP
Glycolysis is the first step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration.
pyruvate: three-carbon molecules produced by glycolysis
phosphorylation: the process of adding a phosphate to a molecule; occurs in cellular respiration and photosynthesis
You consume many complex sugars, like lactose (dairy products) and fructose (fruit), which your body breaks down to glucose that can be used at the cellular level.
All cellular respiration begins with glycolysis. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm. It starts with a 6-carbon glucose molecule and consists of a series of oxidation reduction reactions that essentially split glucose into two, 3-carbon molecules called pyruvate. Pyruvate is then transported into the mitochondria for further processing and energy harvesting or remains available in the cytoplasm for the process of fermentation.
What energy gains are made during glycolysis? Early in glycolysis, two ATP molecules are used to energize glucose to split in two. Glucose is oxidized.
Later, four molecules of ADP undergo phosphorylation to produce four molecules of ATP.
Electrons are donated to two molecules of NAD+ to generate two molecules of NADH. In glycolysis, there is a net energy yield of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
If you need a further explanation of the glycolysis process, read “Outside the Mitochondria: Glycolysis” on pages 183 and 186 of the textbook.
 Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
The “How Glycolysis Works” animation shows how NADH, ATP, and pyruvate are produced during glycolysis.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1. Where does glycolysis occur?
SC 2. Does glycolysis occur without oxygen?
SC 3. What are three products of glycolysis?
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 1. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm.
SC 2. Glycolysis occurs without oxygen.
SC 3. ATP, NADH, and pyruvate are products of glycolysis.