Module 5 Intro
1. Module 5 Intro
1.31. Page 3
Module 5—Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Read
Read
How does looking at the steps involved in aerobic respiration relate to people getting energy to move around? You have followed the path of glucose through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. You have been shown that an electron transport system is where the majority of ATP is synthesized during aerobic respiration. Oxygen is involved in the electron transport system as a final electron acceptor.
The series of reactions involved in aerobic respiration produce large amounts of ATP from just one glucose molecule. As a result, you have energy for activities that you chose and involuntary activity that your body does on its own.
 Watch and Listen
Watch and Listen
This animation will show the final step involved in the synthesis of ATP.
![]() Try This
Try This
TR 1. Comparing Chemiosmosis in Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Chemiosmosis, the movement of hydrogen ions to make ATP, was introduced in Lesson 3 as you learned about photosynthesis. Prepare a list of three similarities and three differences between chemiosmosis in photosynthesis and chemiosmosis in cellular respiration. Your list may include diagrams to illustrate. You may choose to create a slideshow presentation or a podcast of your list. Indicate in the space provided where your teacher may access this activity if it cannot be directly put into this document. Be sure to save your work to your course folder.
Answer this activity in your Lesson 6 Assignment.
 Read
Read
VO2 Max
How have athletes capitalized on understanding the process of cellular respiration?
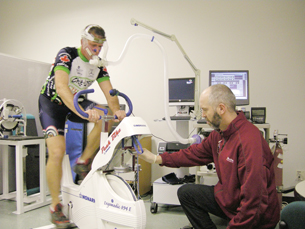
Athletic training programs are designed to increase the body’s ability to deliver and utilize oxygen to become more efficient in the production of ATP. As you saw in Lesson 5, higher levels of physical activity can cause the accumulation of lactate when pyruvate—produced by glycolysis—is not able to be oxidized by the Krebs cycle. The point at which an athlete begins to accumulate lactate in muscle tissues can be used as an indicator of fitness. And this point can also be utilized as a tool for planning further training to improve performance.
Athletes and coaches use a test called VO2 max (the volume of oxygen used at maximal exertion) to determine how well an athlete is able to use oxygen. The test, as shown, is most often conducted in a sports-medicine laboratory because it requires specialized equipment. Although the noted test occurs on a stationary bicycle, the test can also be performed on a running treadmill or on a rowing machine. It is also possible for athletes without the ability to use their legs to do the test by using an arm ergometer or a treadmill adapted for a wheelchair.
During the test, the athlete exercises to exhaustion while the heart rate and chemical composition of inhaled and exhaled air are analyzed. Measuring the quantity of oxygen used by the athlete requires that participants wear a mask to allow inhaled and exhaled gases to be analyzed for their concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The values for VO2 max are expressed as millilitres of oxygen used per kilogram of body mass per minute of activity (mL/kg/min). This technology—based on cellular respiration—helps athletes train and achieve higher levels of fitness.
 Try This
Try This
TR 2. Estimate Your VO2 Max
Caution
If you have a medical condition that prevents you from participating in physical education classes, you should not participate in the exercising part of this activity.
Although a VO2 measurement requires sophisticated equipment, there are a number of methods that you can use to estimate your VO2 max.
In order to estimate your VO2 max, you can perform some sort of physical activity. A simple way to do this is to perform a step test.
To start this test you will require
- a bench or step 12 inches high
- a stopwatch
- a heart-rate monitor (optional)
To conduct this test, you will
- step up and down, one foot at a time, onto the step or bench for 3 minutes
- try to maintain a steady four-beat cycle (approximately 22 to 24 steps/minute)
- use music or counting to help you keep to the required pace
- count your number of heart beats for 15 seconds when you finish the test
- multiply the number of beats in 15 seconds by 4
- repeat this 2 more times
To calculate your VO2 max, you will have to do a websearch using the keywords “VO2 max uk.”
Once you are on a VO2 max website, scroll down to the list of VO2 max tests. Choose a VO2 max step test. Scroll down the page to the Performance Assessment section. Enter your gender and pulse rate. Click on the Calculate button. How well does your body consume oxygen? Use the chart that follows to determine your fitness.
You may also use the “VO2 max from non-exercise data” test.
Female (values in ml/kg/min)
Age |
Very Poor |
Poor |
Fair |
Good |
Excellent |
Superior |
13-19 |
<25.0 |
25.0 - 30.9 |
31.0 - 34.9 |
35.0 - 38.9 |
39.0 - 41.9 |
>41.9 |
20-29 |
<23.6 |
23.6 - 28.9 |
29.0 - 32.9 |
33.0 - 36.9 |
37.0 - 41.0 |
>41.0 |
30-39 |
<22.8 |
22.8 - 26.9 |
27.0 - 31.4 |
31.5 - 35.6 |
35.7 - 40.0 |
>40.0 |
40-49 |
<21.0 |
21.0 - 24.4 |
24.5 - 28.9 |
29.0 - 32.8 |
32.9 - 36.9 |
>36.9 |
50-59 |
<20.2 |
20.2 - 22.7 |
22.8 - 26.9 |
27.0 - 31.4 |
31.5 - 35.7 |
>35.7 |
60+ |
<17.5 |
17.5 - 20.1 |
20.2 - 24.4 |
24.5 - 30.2 |
30.3 - 31.4 |
>31.4 |
Male (values in ml/kg/min)
Age |
Very Poor |
Poor |
Fair |
Good |
Excellent |
Superior |
13-19 |
<35.0 |
35.0 - 38.3 |
38.4 - 45.1 |
45.2 - 50.9 |
51.0 - 55.9 |
>55.9 |
20-29 |
<33.0 |
33.0 - 36.4 |
36.5 - 42.4 |
42.5 - 46.4 |
46.5 - 52.4 |
>52.4 |
30-39 |
<31.5 |
31.5 - 35.4 |
35.5 - 40.9 |
41.0 - 44.9 |
45.0 - 49.4 |
>49.4 |
40-49 |
<30.2 |
30.2 - 33.5 |
33.6 - 38.9 |
39.0 - 43.7 |
43.8 - 48.0 |
>48.0 |
50-59 |
<26.1 |
26.1 - 30.9 |
31.0 - 35.7 |
35.8 - 40.9 |
41.0 - 45.3 |
>45.3 |
60+ |
<20.5 |
20.5 - 26.0 |
26.1 - 32.2 |
32.3 - 36.4 |
36.5 - 44.2 |
>44.2 |
Once you have determined your VO2 max level, consider the following questions before you access your Assignment.
- Were the calculated estimates consistent?
- Suggest reasons why there might be differences between the estimates.
- Were you able to complete the test and, if so, what effect might that have on the value obtained?
- How do you think your value would compare with a VO2 max test performed in a laboratory?
- How does this relate to cellular respiration?
- What does it mean, in terms of aerobic respiration, if your VO2 max value is high?
- What is the relationship between heart rate and cellular respiration?
You will answer similar questions in your Lesson 6 Assignment.
 Discuss
Discuss
How did you do in the VO2 max test? Post reasons why you believe you achieved the score that was estimated and how valuable this kind of test can be. You do not have to post your actual score. See what your peers have to say about their tests.