Module 6 Intro
1. Module 6 Intro
1.4. Page 2
Module 6—The Motor System and Homeostasis
 Explore
Explore
non-striated muscle: contains contractile proteins arranged randomly and do not create bands or stripes; called smooth muscle
striated muscle: marked with stripes or bands that are the result of highly organized arrangements of contractile proteins within muscles
constrict: to make smaller or narrower, especially at one place, by squeezing
Blood vessels will constrict to reduce blood flow.
dilate: to make wider or larger; cause to expand or swell; stretch
Blood vessels will dilate to increase blood flow.
There are three types of muscles in your body. Food moves through intestines and blood moves through blood vessels via the contractions of smooth or non-striated muscle. Your heart, a continually working muscle, beats because of specialized cardiac muscle. The muscles you are most familiar with, like your biceps or abdominals, are skeletal or striated muscles.
One of the major differences between smooth (or non-striated muscles) and cardiac or striated (skeletal) muscles is how they contract. Smooth muscles are said to constrict or dilate, while cardiac and striated (skeletal) muscles contract (shorten) or relax (lengthen). Constriction and dilation are still contractions, but of hollow organs such as your intestines.
 Read
Read
Read “Movement and Muscle Tissue” on pages 332 and 333 of the textbook to compare and contrast the different kinds of muscles.
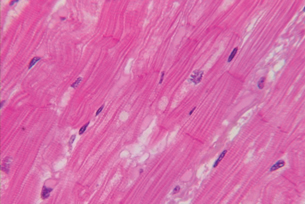
Courtesy of Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
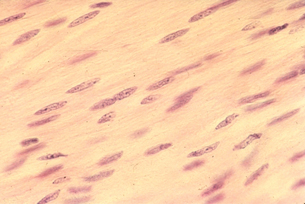
Courtesy of Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
 Try This
Try This
TR 1. Types of Muscle Tissue
You can list the three types of muscle: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Can you differentiate between structure and location in the body?
In the Lesson 1 Assignment you will be asked to summarize the characteristics of each type of muscle and decide how each kind of muscle helps you to react to an event.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1. Click here to complete the Self-Check on muscle types.