Module 7 Intro
1. Module 7 Intro
1.7. Page 5
Module 7—The Digestive and Respiratory Systems
 Try This
Try This
TR 1. Hydogen Peroxide and Catalase
Hydrogen peroxide is a common by-product of certain metabolic reactions that occur in people’s bodies and in the cells of many other plant and animal organisms. The molecule H2O2, despite being formed frequently in human cells, is a toxic metabolite. This means it can be considered a hazardous by-product of normal cellular activities. The toxicity is one of the main reasons why hydrogen peroxide is used to wash cuts or scrapes as an antiseptic. On contact with broken skin, a chemical reaction occurs and with human cells the enzyme catalase is produced to break down the undesirable hydrogen peroxide molecule. The enzyme catalase takes two molecules of hydrogen peroxide and breaks them down into two water molecules and one oxygen molecule. The chemical formula for this reaction is as follows:
2 H2O2(l) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g)−
The following is a three-dimensional image of the enzyme catalase.
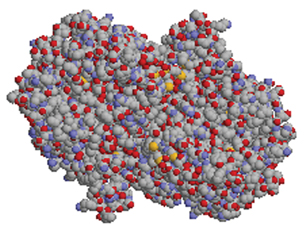
© 2002-2007 Steve Cook
You can observe this reaction first-hand by using hydrogen peroxide from a first-aid kit or purchased from your local pharmacy. You will also require some supplies from your local grocery store or supermarket.
Materials
- pharmaceutical grade hydrogen peroxide (3%)
- beef liver (Chicken liver may be substituted.)
- potato
- glass dish
Procedure
Take a small amount of H2O2—about 5 mL—and add it to a small piece of potato (approximately 1 cm3) in a small test tube or a shallow glass dish. Observe the reaction, and note the products.
Repeat using a 1 cm3 piece of liver. Observe the reaction, and compare it with the previous reaction. Feel the bottom of the test tube or container containing the liver and the H2O2.
Answer the six analysis questions in your Lesson 1 Assignment.