Module 7 Intro
1. Module 7 Intro
1.24. Page 3
Module 7—The Digestive and Respiratory Systems
Respiratory Health
emphysema: an obstructive respiratory disorder in which the walls of alveoli break down and lose elasticity
There are fewer individual air sacs as walls break down, thus reducing the surface area for gas exchange. A loss of elasticity makes exhaling more difficult.
There are diseases specifically associated with the respiratory system. You can have a lower respiratory tract disorder (bronchi, lungs, alveoli) or an upper respiratory tract disorder (nose, pharynx). Some of the diseases are a result of lifestyle choices, such as most cases of emphysema, commonly referred to as smoker’s disease, while other diseases are the result of tumours, bacteria, viruses, or genetics. Medical advances have made it possible to cure some of these diseases. Some diseases, such as emphysema, are incurable but it is possible to treat the symptoms.
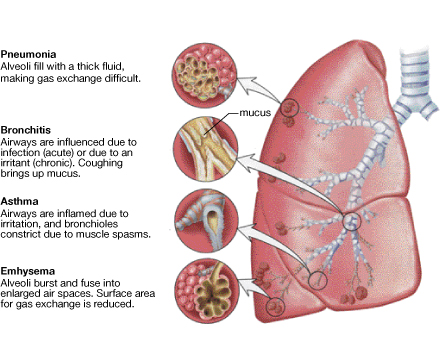
Inquiry into Biology (Whitby, ON: McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2007), 257, fig. 7.8. Reproduced by permission.
 Read
Read
As you read through pages 256 to 261 of the textbook, create a table of common respiratory disorders that lists the symptoms, the cause of the symptoms, how the disorder interferes with breathing, and how each disorder would be diagnosed. You will be using this chart in the next Try This activity.
 Try This
Try This
TR 2. You Diagnose It
Complete “Thought Lab 7.2” on page 261 of the textbook. In this activity you will look at the symptoms of two patients and determine what their disorder may be. You will use your chart of respiratory disorders to aid in making your diagnosis.
Go to your Lesson 4 Assignment to complete this activity.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 1. What is the connection between healthy dietary practices and a healthy functioning body?
SC 2. Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. It occurs when digestive enzymes attack and destroy the pancreas and nearby tissues and cause pain and scarring. Why would a person with pancreatitis have difficulty digesting carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins?
SC 3. Why would restrictive surgery, such as stomach stapling, help an obese person lose weight?
SC 4. Why does pneumonia affect a person’s ability to breathe properly?
SC 5. How does lung cancer interfere with gas exchange?
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 1. Good nutrition is the only way to provide the energy people need to carry out their many activities, such as nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and cell repair and replacement. As well, good nutrition provides the essential raw materials that bodies need as building blocks but are unable to manufacture themselves.
SC 2. A person with pancreatitis would have difficulty digesting carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the small intestine because
-
a lack of trypsin and chymotrypsin would reduce protein digestion
-
a lack of pancreatic amylase would reduce starch digestion
-
a lack of lipase would reduce fat digestion
SC 3. Given that the stomach acts as a reservoir for food during ingestion, restrictive surgery would limit the amount of food that a person could ingest during a meal. With less food entering the digestive tract, caloric intake would be reduced and result in weight loss.
SC 4. Pneumonia is a disease that occurs when the alveoli in the lungs inflame and fill with liquids. This interferes with gas exchange, and the body becomes oxygen-starved.
SC 5. Lung cancer diminishes gas exchange because tumours destroy healthy areas of the lung. This reduces the surface area for gas exchange. Alveoli can be damaged and allow fluids, such as blood, to fill up air sacs and reduce gas exchange.