Module 5
1. Module 5
1.29. Page 4
Module 5—Cell Division: The Processes of Mitosis and Meiosis
 Self-Check
Self-Check
In this lesson you have learned about the diversity of reproductive strategies for a range of organisms. You can appreciate the variety of ways species balance their life cycles. To apply your understanding, complete the following questions.
Use the following information to answer the next question.

SC 11. Which structures in the life cycle of Ulva are haploid (monoploid)?
A. zoospores and the zygote
B. the sporophyte and the zygote
C. zoospores and the gametophytes
D. the sporophyte and the gametophytes
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
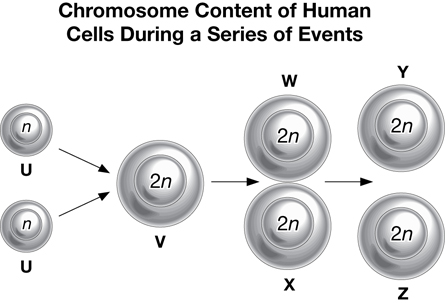
SC 12. In humans, what process must have occurred to obtain the cells at U?
A. mitosis
B. meiosis
C. fertilization
D. differentiation
SC 13. In humans, what process must occur before cell V forms cells W and X?
A. mitosis
B. meiosis
C. recombination
D. nondisjunction
Use the following information to answer the next question.

Numerical Response
SC 14. Identify the stages in the conifer life cycle, as numbered below, that correspond with the letters that represent the stages on the diagram.
Stages in the Conifer Life Cycle
- haploid stage
- diploid stage
Stages: _____ _____ _____ _____
Diagram: A B C D
Use the following information to answer the next question.
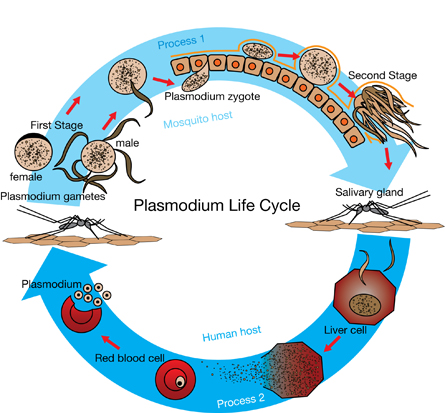
SC 15. Identify the row in the table below that identifies the chromosome number at the first stage and the chromosome number at the second stage.
Row |
First stage |
Second stage |
A. |
diploid |
haploid |
B. |
diploid |
diploid |
C. |
haploid |
diploid |
D. |
haploid |
haploid |
SC 11. C
SC 12. B
SC 13. A
SC 14. 1, 1, 2, 2
SC 15. C
 Reflect on the Big Picture
Reflect on the Big Picture
In this lesson you have looked at a variety of life cycles found in organisms. Each cycle balances the speed and ease of mitosis with the variety and change of meiosis. Earlier you learned how those processes result in cells for growth or gamete cells for reproduction. When you completed “Thought Lab 16.2: Comparing Reprodcutive Strategies” for the Lesson 6 Assignment, you conducted research on two organisms and their reproductive strategies. You related the processes of mitosis and meiosis to the various reproductive cycles of the different organisms of your choice.
The Module Assessment is described in the Module Summary and Assessment section. In the Module Assessment, you will examine normal growth, repair, and reproduction in cells and organisms. You will also look into exceptions to normal cellular patterns and evaluate their impact. You will again have an opportunity to apply the patterns you explored in this lesson to your work in responding to your choice of the options provided in the Module Assessment.
 Module 5: Lesson 6 Assignment
Module 5: Lesson 6 Assignment
Submit your completed Module 5: Lesson 6 Assignment to your teacher for assessment.