Module 1
1. Module 1
1.5. Page 3
Module 1—Momentum and Impulse
Momentum and Newton’s Second Law
Recall that Newton’s second law states that if an external, non-zero, net force acts on an object, it will accelerate. Acceleration means a change in velocity, which means a change in momentum! The external unbalanced force, therefore, causes a change in momentum. In other words, if there’s an ![]() , there’s a
, there’s a ![]() . Therefore, Newton’s second law and momentum are related to one another.
. Therefore, Newton’s second law and momentum are related to one another.
 Read
Read
Find out more about the connection between momentum and Newton's second law of motion by reading pages 450 to 452 in your textbook.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 7. Show the derivation of Newton's second law in terms of the change in momentum.
 Self-Check Answer
Self-Check Answer
SC 7.
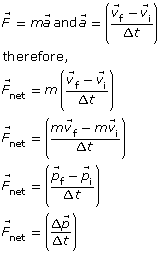
![]()
In this form, Newton’s second law tells us that the external, non-zero, net force acting on an object will be equal to the rate of change of the momentum of that object with respect to time. For example, in order to change the momentum of a large mass, such as a passenger car (even if it is moving at a low velocity), in a short time, a very large net force will be required. The same is true for a smaller mass, such as a motorcycle if it travels at high velocity. In this form of Newton’s second law, the mass, the time interval and the velocity of the object (momentum) are considered.
 Reflect and Connect
Reflect and Connect

© Mikael Damkier/shutterstock
A moving vehicle has a momentum defined by the product of its mass and velocity. Changing either of these two quantities will cause a corresponding change in the momentum. Both the mass and average velocity of modern vehicles is much larger than those of the past. This means that the amount of momentum on today’s busy freeways is increasing. And according to Newton’s second law, a large net force is required to make a large change in momentum quickly. In effect, this means that the modern car crash that involves a larger vehicle and/or one travelling at a high velocity will generate larger net forces since the time of the collision hasn’t changed.
Can you think of what implications this has for both vehicle design and safety? Larger vehicles and/or those that travel at a high rate of speed require larger engines and brake systems and stronger steering systems. All of these design features are required to change large amounts of momentum in short periods of time.
 Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to D 1 or D 2 or D 3 to your teacher as part of your Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment.
 Discuss
Discuss
In the discussion forum, use the concepts of momentum and Newton’s second law to explain why the following statements are true.
D 1. A large freight train moving down the tracks takes a long time to stop.
D 2. A motorcycle can have the same momentum as a large truck.
D 3. In general, a motorcycle can accelerate at a greater rate than a large truck.
You may want to review the discussion rubric for the assessment criteria in posting and responding to discussions.
| Principles involved: momentum | ||||
Criteria |
Level 1 (Below Standard) |
Level 2 (Approaching Standard) |
Level 3 (Standard) |
Level 4 (Above Standard) |
| Knowledge | ||||
| Demonstrates understanding of the situation, physics principles and technology, and their connections. | Demonstrates a vague and sometimes incorrect understanding of the physics principles involved. Obvious irrelevant or missing information. | Demonstrates a basic understanding of the physics principles involved. May exhibit minor mistakes or vague information or application to the situation. | Demonstrates a good understanding of the physics principles involved and applies them properly to the given situation. All necessary information is given. | Demonstrates a superior understanding of the physics principles involved and their application to the situation. All applications are considered in detail. |
| Reflection | ||||
| The post shows reflection on one’s own and other students’ work. Contributes to the group discussion. | Does not make an effort to participate. Seems indifferent to discussion. | Occasionally makes meaningful reflections on the group’s efforts or discussions. Marginal effort is shown to become involved with the group or discussion. | Frequently makes meaningful reflections on the group’s efforts and presents relevant viewpoints for consideration by the group. Interacts freely with group members. | Regularly attempts to motivate the group discussion and delve deeper into concepts. Interacts freely and encourages all group members. |
| Content and presentation of discussion summary | ||||
| The information is logically arranged in a clear and concise manner. | The information is poorly organized with many concepts implied. Irrelevant or rambling sentences make reading difficult. | The information is somewhat organized with implied concepts. Excessive words or awkward sentences are used, which hinder reading. | The information is well-organized and logically arranged. All concepts are explicitly explained. There are a few awkward but understandable sentences. | The information is well- organized and very easy to understand. Well-worded sentences make reading pleasurable. |
Once you have submitted your explanations, read at least two other postings. Consider how well these responses used the concepts of momentum and Newton’s second law. Reflect on your responses and the two others you have read. Choose one of the responses, revise your response and submit both the original and the revised response to your teacher.
 Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to Reflect on the Big Picture to your teacher as part of your Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment.
 Reflect on the Big Picture
Reflect on the Big Picture

© Radu Razvan/shutterstock
In real life, a police officer may warn that “speed kills.” In video games, high-speed crashes are common. Suppose a particular scene in a game requires the following elements:
-
A high-performance motorcycle must crash into a barrier and be stopped.
-
A small scooter must crash into another section of the same barrier and be stopped.
-
The forces exerted as each vehicle collides with the barrier change the shape of that section of the barrier in addition to stopping the vehicle.
-
The time required to stop each vehicle must be realistic.
Create a paragraph, illustration, animation, or audio recording to explain how you could use the concept of momentum and net force to make each simulated crash realistic. In general, how could you use momentum and Newton's laws of motion to predict the amount that each section of the barrier changes shape?
Store your completed reflection in your Physics 30 course folder, and submit your creation to your instructor for marking.
 Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
Submit your responses to the following parts of your Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment to your teacher:
- Module 1: Lesson 1 Assignment
- Assignment —A 1, A 2, A 3, A 4
- Discuss—D 1, or D 2, or D 3
- Reflect on the Big Picture
 Lesson Summary
Lesson Summary
In this lesson you explored the following questions:
-
What is momentum?
-
Why is momentum defined as a vector?
-
How is momentum related to Newton’s laws?
Momentum is the product of an object’s mass and velocity.
Since momentum is the product of a vector (velocity) and a scalar (mass), it is a vector quantity. The direction of the momentum vector is in the same direction and is relative to the same reference frame as the velocity of the object.
Newton’s second law tells us that the external, non-zero, net force acting on an object will be equal to the rate of change of the momentum of that object with respect to time. This has particular relevance to situations involving large changes in momentum, such as those of vehicle collisions. In the next lesson you will learn how effective vehicle safety devices can be designed based on the same principles.
Lesson Glossary
momentum: is the product of the mass and velocity of an object
Expressed as an equation it is