Lesson 4: Chemical Bonding and Diversity of Matter
5. Electronegativity and Polarity
A polar covalent bond is formed when electrons between two atoms are not shared equally. The electron with higher electronegativity is partially negative, δ-, and the one with lower electronegativity is partially positive, δ+. For example, in the bond between O and H, O has a higher electronegativity and is δ-, while H is δ+. 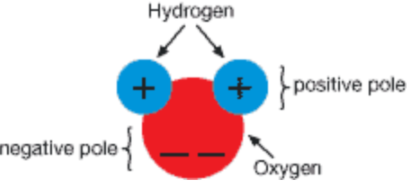
δ- ←l- δ+
O - H
3.4 - 2.2
The arrow from the diagram above represents a bond dipole, where the arrowhead is the negative end and the tail is the positive end of the polar covalent bond. It is important to note that the general trend for electronegativity is as shown in the chart below.
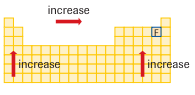
Also, study the empirical rules for polar and nonpolar molecules in the following table:
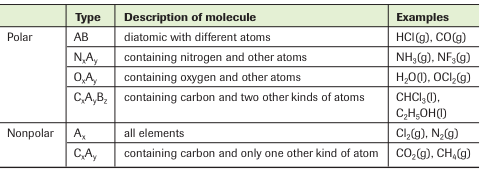
The table is certainly a great tool to determine the polarity of molecules. However, sometimes we might have to make use of other theories such as Lewis symbols and VSEPR theory to determine the polarity of molecules. Watch the video below to see how.