Lesson 1. Solutions and Molarity
2. Energy Changes and Electrolytic Solutions
Endothermic vs. Exothermic Reactions
Breaking bonds is always endothermic while forming bonds is always exothermic. There are two major steps when a solute dissolves in water.
- Endothermic process: energy is being absorbed to break the individual ions that formed the crystal lattice within that ionic solid.
- Exothermic process: energy is released from the system as the individual ions now are surrounded by water molecules.
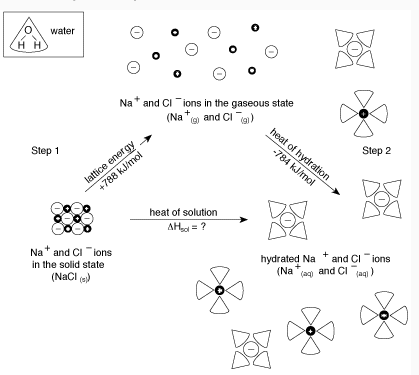
The overall process can be summarized by the following equation:
Final Energy= (Energy to break apart solute) + (Energy to bind solute ions to water)
- Energy absorbed to break apart the solute < the energy released as the ions bind to water. The overall process of dissolving is Exothermic
- Energy absorbed > the energy released. The overall process of dissolving will be endothermic.
Can you tell if the reaction shown from the diagram above endothermic or exothermic?
NaCl(s) + 788 kJ/mol → Na+(g) + Cl-(g) ( Endothermic)
Na+(g) + Cl-(g) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + 784 kJ/mol (Exothermic)
Since the Net Energy = 788 kJ/mol - 784 kJ/mol= 4 kJ/mol, this reaction is endothermic reaction.
Electrolytic Solutions
Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Electricity flows from one location to another through a conductive substance that acts as a medium through which electrons can travel.
Metals are often good conductors because they tend to form lattice structures that make it very easy for electrons to bounce from atom to atom in a current. The conductivity of solutions is determined by the concentration of ions dissolved in the solution. The more positivity and negatively charged particles there are in the solution the greater the conductivity will be.
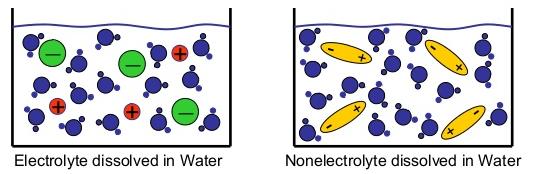
Nonelectrolytes do not conduct electricity when dissolved in water because they are electrically neutral molecules. Ionic compounds are electrolytes. Most molecular compounds are nonelectrolytes, but there are a few exceptions, such as organic acids, and some dissolved gases, like carbon dioxide in an aqueous solution. Acids, bases, and salts form ionic bonds which makes them electrolytes. Substances that form covalent bonds are either nonelectrolytes or poor electrolytes.